Miniature model, a more manageable version of something much bigger in your hands, has an unexpectedly appealing quality. Thus, a scaled-down model does just that: it transforms an imaginary world, data, and design into something you can immediately see, touch, explain, and understand. However, its uses go well beyond aesthetics; miniature model-making is becoming increasingly useful in all spheres of life, enabling people to test ideas early on, communicate ideas more effectively, and most importantly, make better decisions and reduce the product manufacturing time.
Making miniature models is not just about craftsmanship; it’s also about storytelling, acknowledging, precision, and purpose.
Miniature model making involves building replicas of objects, structures, or systems as physical models from which the final product is to be designed. These are highly detailed models that are made to scale with the design's form, proportions, and functionality based on the original design.
Historically, miniatures were made by hand out of wood or clay, sometimes foam. Nowadays, these options have been highly broadened by modern technologies such as 3D modeling and 3D printing, laser cutting, and CNC machining, which have significantly broadened the options available, leading to more precise models, increased production speed, and even geometries that were previously unattainable.
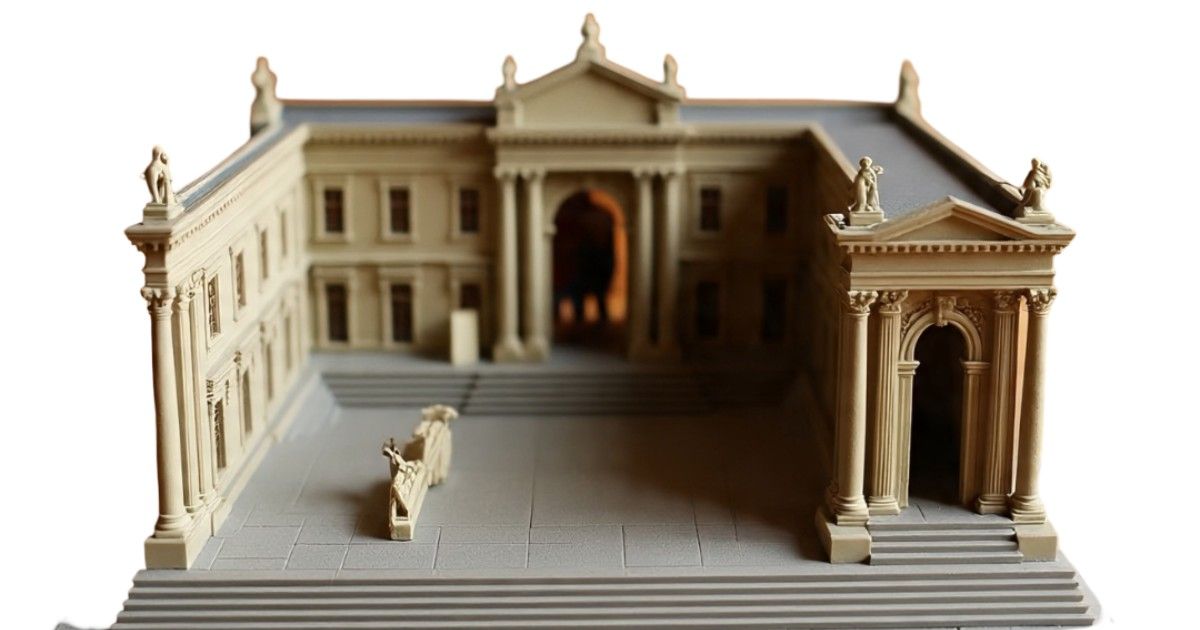
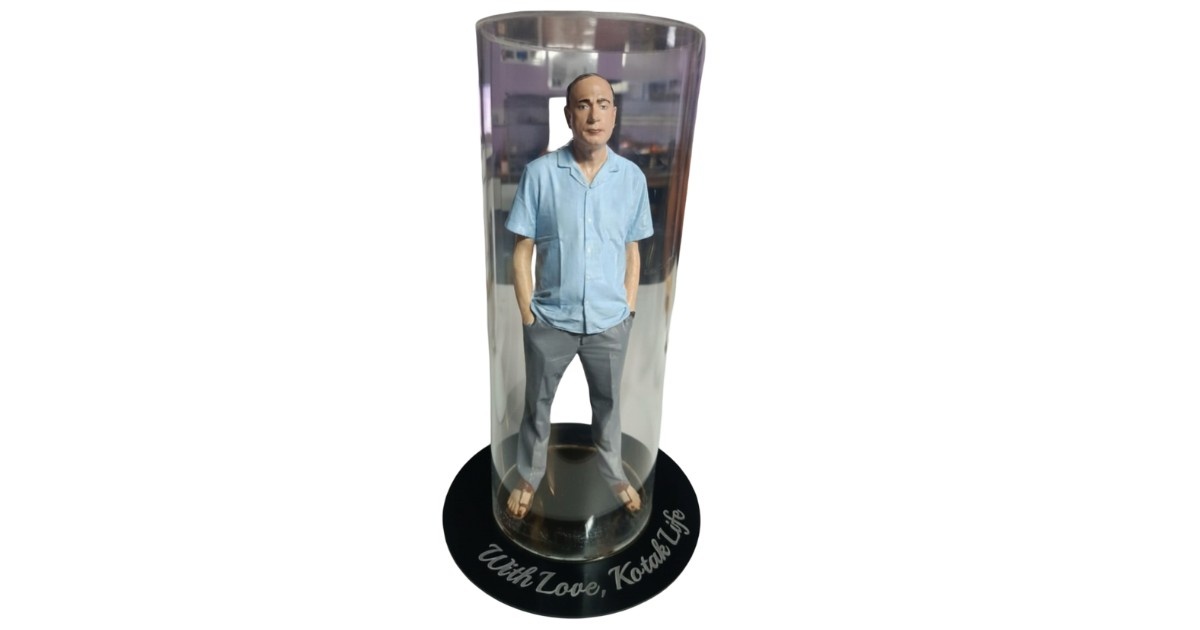


Making 3D miniatures, 3D-printed parts, or prototype models is a potent tool that bridges the gap between technology, creativity, and real-life experience. It is essential to contemporary design and communication because of its applications in architecture, engineering, education, marketing, and industrial design. The impact and potential of 3D miniature or 3D printing models will only increase as digital design and 3D printing technologies advance
RA Global Tech Solutions has successfully delivered over 2000 miniature models across diverse sectors, including medical, gaming, and artifacts. Additionally, we support manufacturing batches for real-life applications. At RA Global Tech Solutions, 3D-printed functional models have been supplied to clients in Muscat, the United Kingdom, and the UAE.
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a profound transformation with the rise of on-demand advanced manufacturing. This innovative approach is reshaping how products are designed and manufactured, delivered and empowering industries to respond swiftly to evolving market demands.
On-demand advanced manufacturing leverages cutting-edge technologies such as 3D printing, investment casting, CNC machining, and rapid prototyping to manufacture products quickly and efficiently. Often used for small batches or one-off quantities, this approach reduces inventory costs, accelerates production timelines, and enhances product quality.
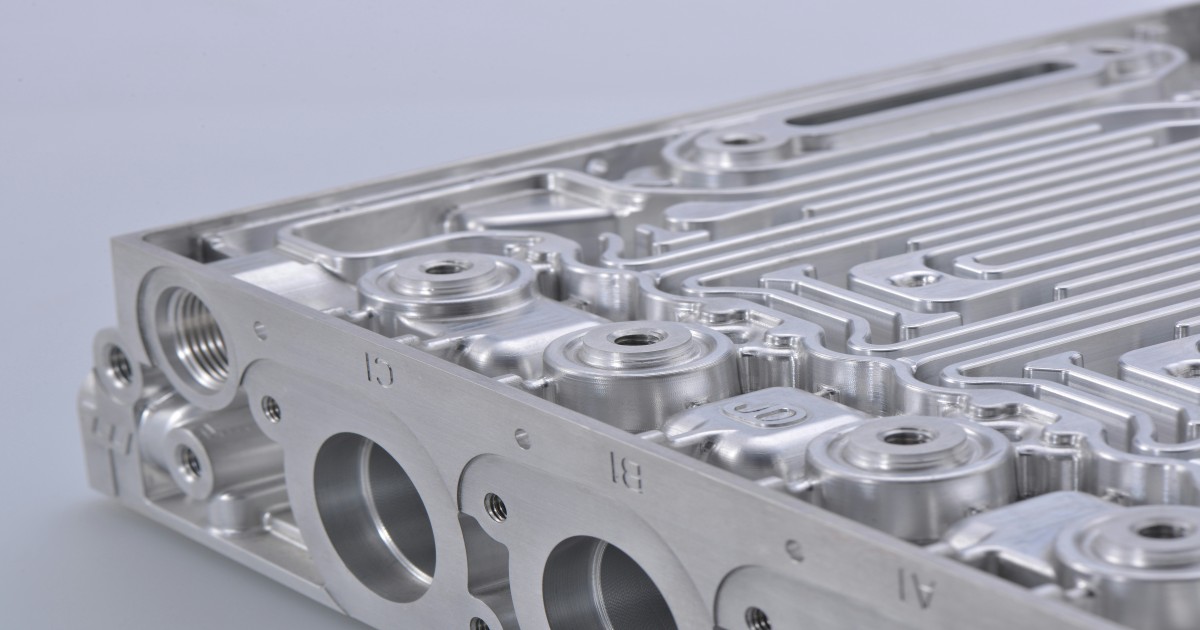
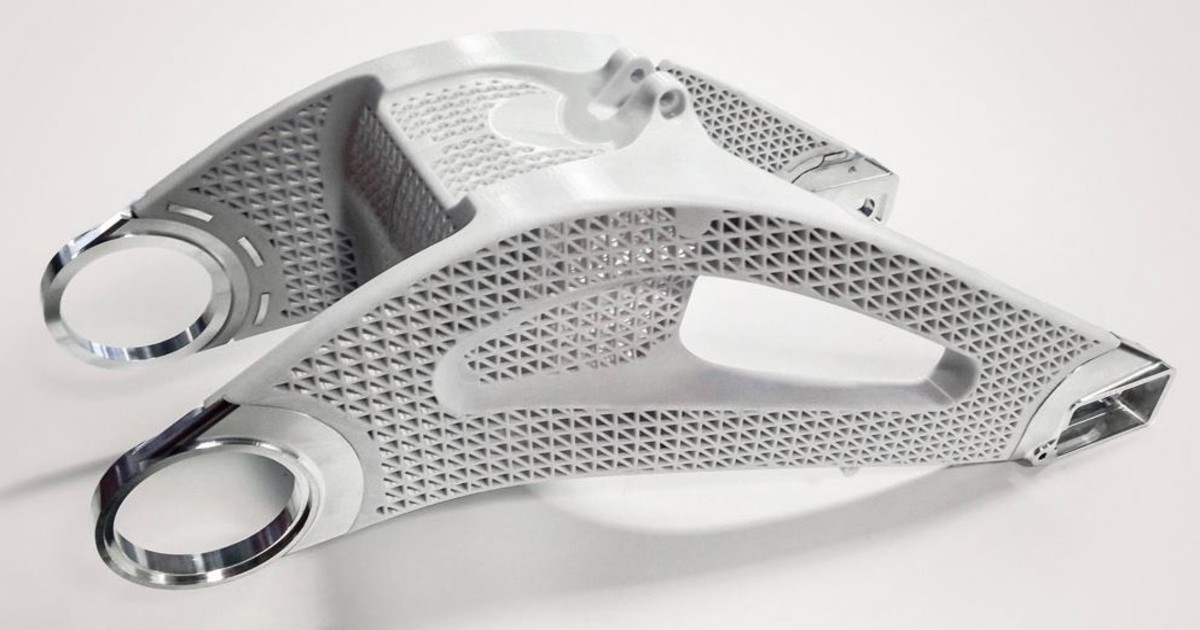


At RA Global, we offer on-demand advanced manufacturing services that help industries innovate and scale up their production needs. Using state-of-the-art technologies, including 3D printing, investment casting, CNC machining, and rapid prototyping, our team delivers high-quality products and tailored solutions that meet the unique demands of each client.
On-demand Advanced manufacturing is transforming the way industries operate, offering greater flexibility, reduced costs, and superior product quality. At RA Global, we are all about leveraging tech like 3D printing, investment casting, CNC machining, and rapid prototyping to drive innovation, efficiency, and growth for our clients.
In the fast-paced world of technology, innovation and vision are the driving forces behind successful companies. RA Global Tech is one such company that has turned its vision into reality, providing cutting-edge technology solutions to businesses worldwide. Let us take a closer look at the story of RA Global Tech Solutions LLP and how it has evolved from an idea to a thriving technology company.

In 2017, RA Global Tech Solutions embarked on a remarkable journey, fueled by a vision to bridge the gap between technology and innovation. From a small office space with just one PC, the company has grown into a trusted partner for businesses across various industries.
With a team of passionate and experienced engineering professionals, RA Global began its quest to deliver tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of its clients. From concept to commissioning, the team ensured seamless execution and exceptional quality, laying the foundation for long-term partnerships with clients.
As the company grew, so did its expertise. The RA Global team expanded, and its capabilities evolved to include
Through its journey, RA Global has remained committed to delivering value to its clients. By fostering strong partnerships and providing exceptional solutions, the company has established itself as a leader in the engineering services industry.

By partnering with RA Global, businesses can unlock the potential of trusted engineering solutions and services, transforming ideas into tangible successes.
Driven by a relentless pursuit of engineering excellence, RA Global Tech Solutions operates as a trusted partner to some of the world's most influential brands across multiple industries, including automotive, aerospace and defense, medtech and healthcare, energy, and more. At the heart of RA Global's approach is a conviction that true engineering transformation comes from partnership. Rather than offering transactional support, the company embeds engineering teams inside client ecosystems through what it calls Virtual Business Units (VBUs). These dedicated teams are empowered to make decisions at speed, collaborate across time zones, and co-create custom solutions at the source of the client need. Whether designing innovative product solutions, optimizing complex systems, or building predictive models, RA Global delivers full lifecycle engineering solutions. With expertise spanning various domains, RA Global is committed to driving engineering excellence and delivering value to its clients. By partnering with RA Global, businesses can unlock the potential of trusted manufacturing solutions and services, transforming ideas into tangible successes.
Our journey began with a vision to bridge the gap between technology and innovation. We have worked tirelessly to make that vision a reality, delivering high-end engineering services that drive innovation and growth. With a team of experienced engineers and experts, we have provided tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of our clients. Our mission is to empower businesses with cutting-edge engineering solutions that enhance their competitiveness, efficiency, and sustainability. We strive to deliver exceptional value to our clients, partners, and stakeholders through our expertise, creativity, and commitment to excellence. At RA Global Tech Solutions, we are dedicated to delivering innovative engineering solutions that drive growth and excellence. With our expertise, commitment to quality, and customer-centric approach, we are confident that we can help businesses achieve their goals.
In recent years, 3D Printing has emerged as a transformative force in various sectors around the globe, and India is no exception. India's 3D printing industry is gaining traction, transitioning from prototype-focused applications to end-product manufacturing, driven by reduced costs and accelerated by AI integration.
Agnikul, a Chennai-based spacetech firm, made history with the world's first rocket launch powered by a single-piece 3D-printed engine. What's remarkable is that they achieved this feat in just three days, a significant reduction from the typical 10-11 months of preparation time, where manufacturing a rocket engine alone usually takes six months. This innovation greatly cut down time, effort, and costs.
India's 3D printing market is gaining momentum, with diverse applications emerging across industries. According to IMARC Group, the Indian 3D printing market, valued at $707 million in 2024, is projected to reach $4.3 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 21.7%.
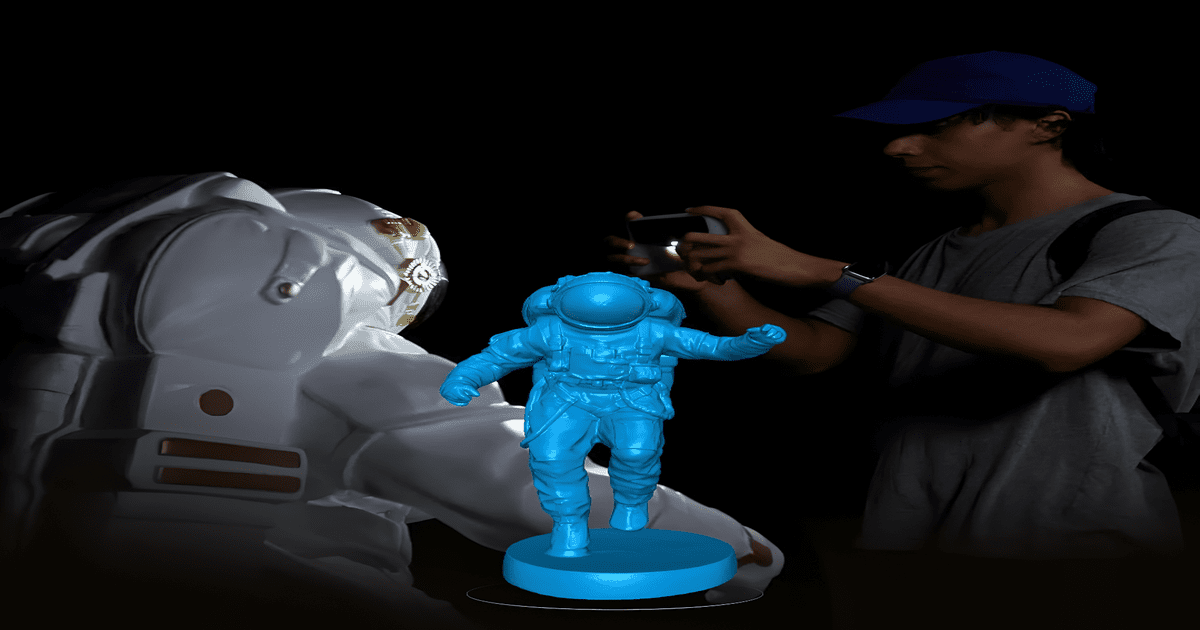

The toy industry is another area where 3D printing is making waves, allowing for designs that were previously impossible or prohibitively expensive to produce. Customizable toys that reflect the preferences of individual consumers are becoming increasingly popular, thanks to this technology. For example, parents can now design toys tailored to their children’s interests, which adds personal value to the products.
This shift toward customization is not only enhancing consumer satisfaction but also promoting a culture of creativity and innovation among young creators and entrepreneurs in India.
RA Global offers various services that can support the implementation of Rocket Fuel to Playful Tools, including
Despite the exciting developments, challenges remain. One significant hurdle is the need for skilled labor capable of operating advanced 3D printing technologies and software. Therefore, educational institutions and industry must collaborate to develop specialized training programs to build a proficient workforce.
Furthermore, regulatory frameworks need to evolve to address intellectual property issues associated with 3D printing. As the technology becomes mainstream, safeguarding innovation while fostering collaboration will be essential for sustained growth.
The 3D printing industry is shifting towards more sustainable raw materials, moving beyond traditional plastics and polymers to eco-friendly options like biodegradable cornstarch. This global trend towards environmentally responsible alternatives is being actively adopted in India.
3D printing is poised to be a catalyst for India’s industrial renaissance, fundamentally changing the way products are designed and manufactured across numerous sectors. From aerospace to consumer goods, the applications of this technology are vast and varied.
As we embrace these advancements, India stands at the threshold of a manufacturing revolution—one that has the potential to stimulate economic growth, encourage entrepreneurship, and position the country as a leader in the global market. The possibilities are limitless, and as 3D printing continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of Indian industry.
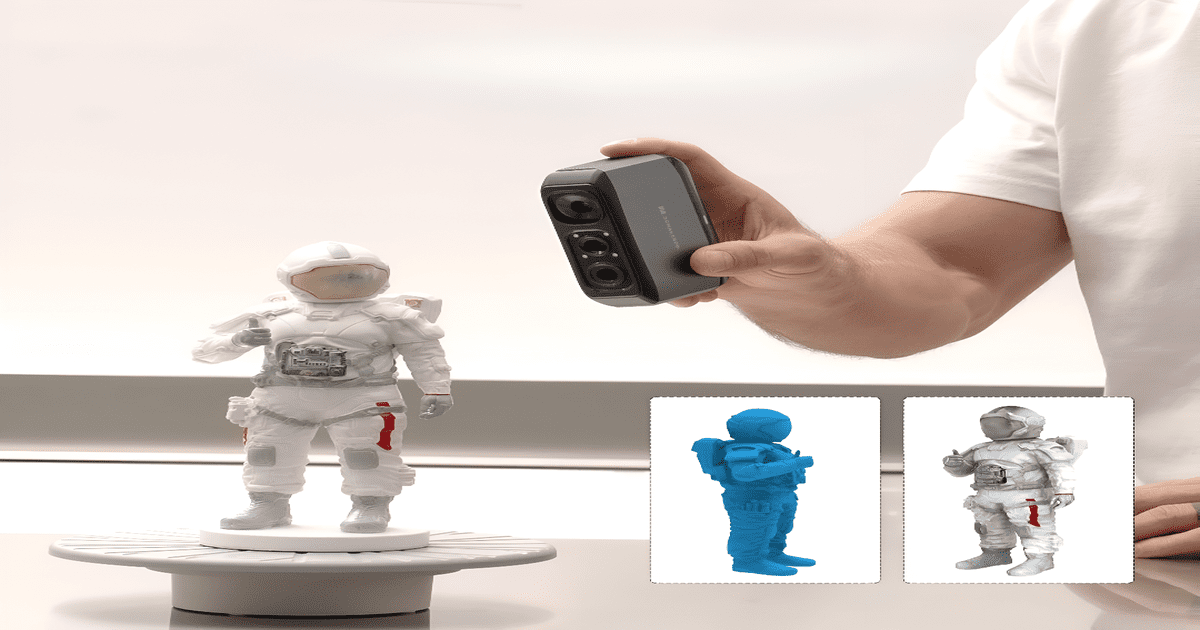
3D laser scanning technology has completely changed how industries collect, analyze, and interpret physical data. Whether it is applied to engineering, manufacturing, construction, or even preservation, 3D laser scanning provides unmatched accuracy and efficiency when mapping intricate geometries. As industries increasingly adopt this advanced technology, it's clear that 3D laser scanning is becoming a key tool for many professionals worldwide.
At its core, 3D laser scanning is a process that uses 3D lasers to capture a physical object’s shape, dimensions, and spatial orientation in high detail. The technology works by emitting a 3D laser source onto an object and measuring the reflection to generate thousands or even millions of precise data points. These points are then compiled to create a point cloud, which is a highly accurate digital representation of the 3D scanned object or environment.
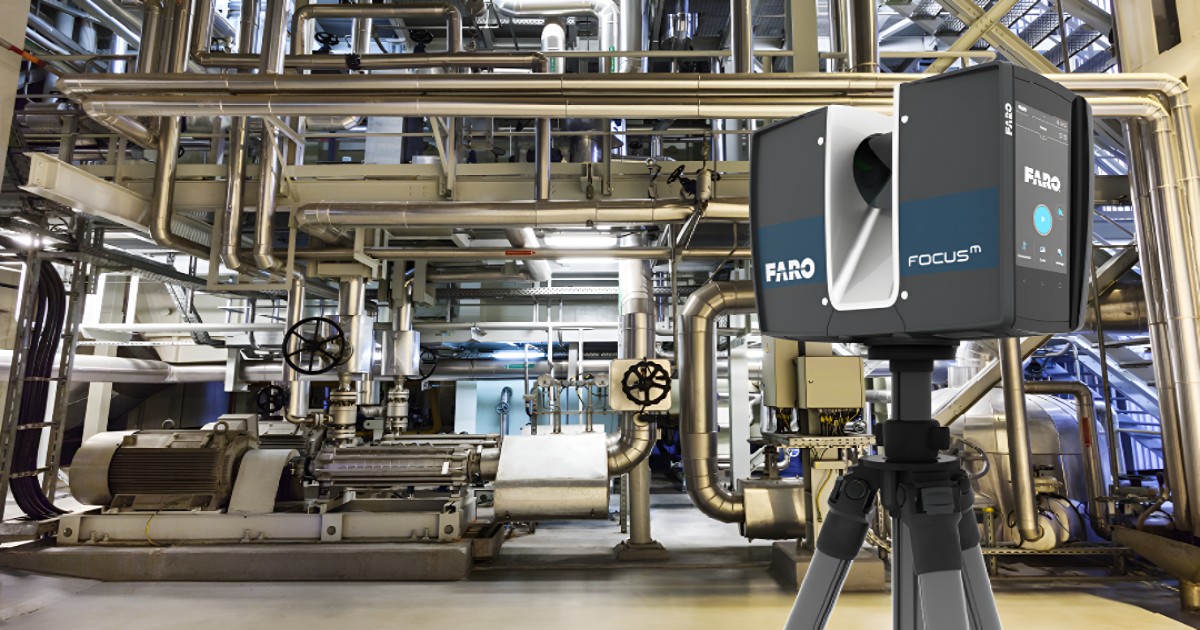

Precision and preciseness: The great accuracy offered by 3D laser scanning is among its most important benefits. Human error is frequently a possibility with traditional methods of mapping and measuring objects, but 3D laser scanning removes this issue. Even the smallest details can be captured by the technology, guaranteeing accurate measurements that are crucial for projects that need precise specifications.
Efficiency in data collection: 3D laser scanning is incredibly efficient when it comes to collecting large amounts of data in a short time. In industries where time is of the essence, such as industrial design and construction, this is particularly helpful. As opposed to the hours or days that manual measurement typically takes, it can be finished in a fraction of the time without compromising accuracy.
Architecture and construction: Used for designing blueprints or retrofitting projects.
Manufacturing: Helps in reverse engineering parts or ensuring product quality.
Cultural heritage: For preserving historical monuments and artifacts.
Healthcare: Assists in creating custom prosthetics or anatomical models.
3D Scanning the object or environment: The 3D laser scanner is set up at a fixed location. After that, it starts to shoot laser beams that move over the target object. A data point is gathered each time the laser strikes a surface, depending on the angle and distance of the reflection.
Creating a point cloud: As the 3D scanner moves, it gathers millions of these points, creating a point cloud. This cloud forms a highly detailed, three-dimensional digital model of the 3D scanned object or environment.
Post-processing and analysis: Once the point cloud is generated, it is transferred to specialized software where it can be manipulated for various uses. Engineers, architects, or designers can then analyze the model for any necessary modifications or measurements.
Construction and architecture: In construction, 3D laser scanning is a valuable tool for designing and planning structures. It can swiftly map out expansive spaces or existing structures, giving construction teams access to extremely precise data. Errors are decreased, and improved project management is made possible.
Manufacturing and reverse engineering: 3D laser scanning plays a pivotal role in reverse engineering. By 3D scanning existing parts or prototypes, manufacturers can recreate designs, perform quality checks, or improve upon existing products. This is essential for industries like automotive or aerospace, where precision is key.
Preservation and restoration: For museums and cultural institutions, 3D laser scanning is an excellent tool for preserving historical artifacts. It allows for detailed replication and conservation of ancient buildings or sculptures, ensuring that cultural heritage is maintained for future generations.
In terms of accuracy, speed, and versatility, 3D laser scanning is simply superior to conventional measurement techniques like tape measures and digital calipers, which have been in use for centuries. Laser scanning is the more effective and dependable option for complex projects because it can collect data from hard-to-reach places and is less likely to make mistakes.
As technology evolves, 3D laser scanning is only expected to become more advanced. Innovations such as faster scanning times, improved portability, and integration with other technologies like artificial intelligence or augmented reality will likely make this technology even more indispensable across various industries.
In conclusion, 3D laser scanning is a useful tool in sectors like manufacturing, cultural preservation, and construction because of its many advantages. It is a worthwhile investment for businesses trying to streamline their operations and lower human error because of its quick turnaround time and capacity to provide accurate, comprehensive data.
If you want to use innovative techniques for your projects, think about utilizing 3D laser scanning to reach new levels of accuracy and productivity.
Additive manufacturing (AM) was invented in the mid-1980s in Japan, after which it soon became well-known for rapid prototyping all over the world. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a technology that builds objects by adding material layer by layer. Materials used in this method can range from plastics, metals, ceramics, and cement, amongst many others. Today, it is being utilized in several industries: aerospace, healthcare, automotive, construction, and manufacturing to produce final product parts. This method has become more tangible in recent years and is the future for engineers and the manufacturing industry.
Bringing additive manufacturing into mainstream bulk manufacturing will shockingly reduce production costs while simultaneously improving the quality of the product. Unlike traditional methods of manufacturing, additive manufacturing does not require the building of molds or any special machinery; a single Computer-Aided Design software file is the only pre-production element necessary.
A single additive manufacturing machine is capable of working with different materials to produce a vast array of products, hence reducing investment costs greatly. Labor costs are relatively low, as there is no requirement for assembling, as the product is made as a single part. The quality of the product is much superior, as materials such as carbon fibers and titanium can be integrated easily into the product. The entire process of making a finished product has no human interference, hence eliminating the possibility of any human error that may occur during a traditional manufacturing process and also increasing the rate of production by several folds.

Traditionally, a manufacturer's production ability would decide the structural design of the product. But with the introduction of 3D printing services, the power is in the hands of engineers, and they have total liberty to design as they envision the product. Customization of products based on the customers' needs at lower costs is a much more plausible concept with 3D printing. Professionals in the healthcare industry are looking to create replacement parts and bones specific to their patients' needs for a higher success rate and reduced infections. This technology is also proving to be a game-changer for the aerospace industry, as lighter but more durable parts can be made. In space astronauts and engineers use 3D printing to print crucial parts in case of emergencies. Another impeccable feature of additive manufacturing technology is that modifications and adjustments to the product design can be made at any moment without increasing costs or slowing down the production process.
The environment also benefits greatly from this process. Due to the lack of raw materials needed to mold or color the product, there is a significant drop in the waste generated. Often machines also release toxic waste while producing products, which is then released into freshwater bodies and oceans, causing water pollution. Some products made by traditional machines also require burring and heating, which release toxins into the air. With the use of 3D printing, no materials are wasted and no form of pollution is caused.

There are several challenges to the scaling of 3D printing to become the new ordinary form of production. There needs to be more research and development done in this area to improve upon materials and efficiency and reduce initial setup costs. Engineers need to be more open to experimenting and educating themselves about additive manufacturing, and countries need to improve their digital framework to ensure the success of this promising method. Several hurdles stand in the way of the success of this manufacturing method, but it is capable of being the next industrial revolution that will benefit consumers, business owners, and the environment alike.
The first modern car was invented in the mid-1880s, and we have come a long way since. Innovation has been booming in the automotive industry as fierce competition motivates companies to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction. Assembly lines and structural and functional changes have consistently been made to engines and the exteriors of vehicles, but the next biggest change due to innovation is going to be the way the automotive industry manufactures its cars.
3D printing, a method commonly used in the automotive industry to make prototypes, is currently in the driver’s seat, steering the world of automobiles to a future that was never anticipated before. 3D printing is a method of manufacturing where digital files are converted to three-dimensional objects, using different materials and printing layer by layer.
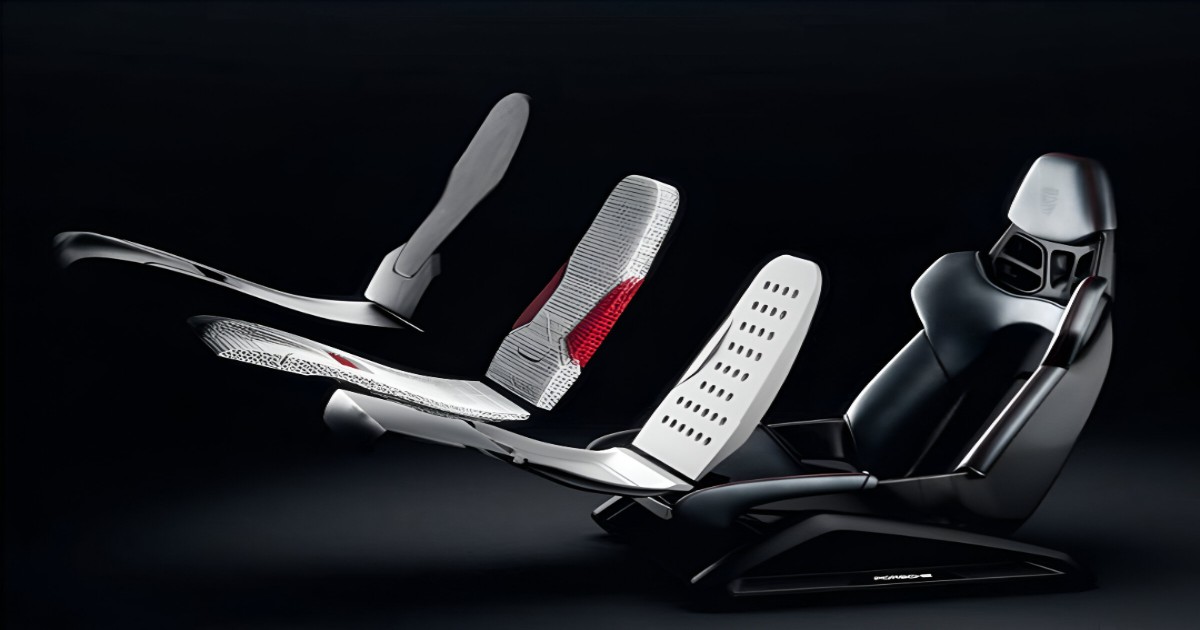

The potential of this technology has no bounds in the automotive world. Today, 3D printing is pivotal in the product design and development process, as it rapidly allows engineers to produce prototypes and simultaneously also enables them to make revisions to their designs on the go at a low cost. The flexibility of this manufacturing process in the future will benefit mass production, as companies will be able to fix issues without the need to change the assembly lines. In today’s highly customer-centric market, this feature will be rather valuable, as customers will be able to customize the exterior as well as the interior of the car at an affordable cost.
The main point of distress for the automotive industry is often the cost of production and its efficiency. 3D printing can benefit both these aspects and beyond. This method delivers the product in its complete form, requiring a smaller number of parts to be assembled, improving efficiency, and reducing labor costs. A company called Local Motors developed a car called Strati that is the world’s first car to be built using 3D printing technology. 75% of this car is printed, while as opposed to the regular 2000 components, there are only 57 components that are required to be assembled for this car (Barker, 2016).
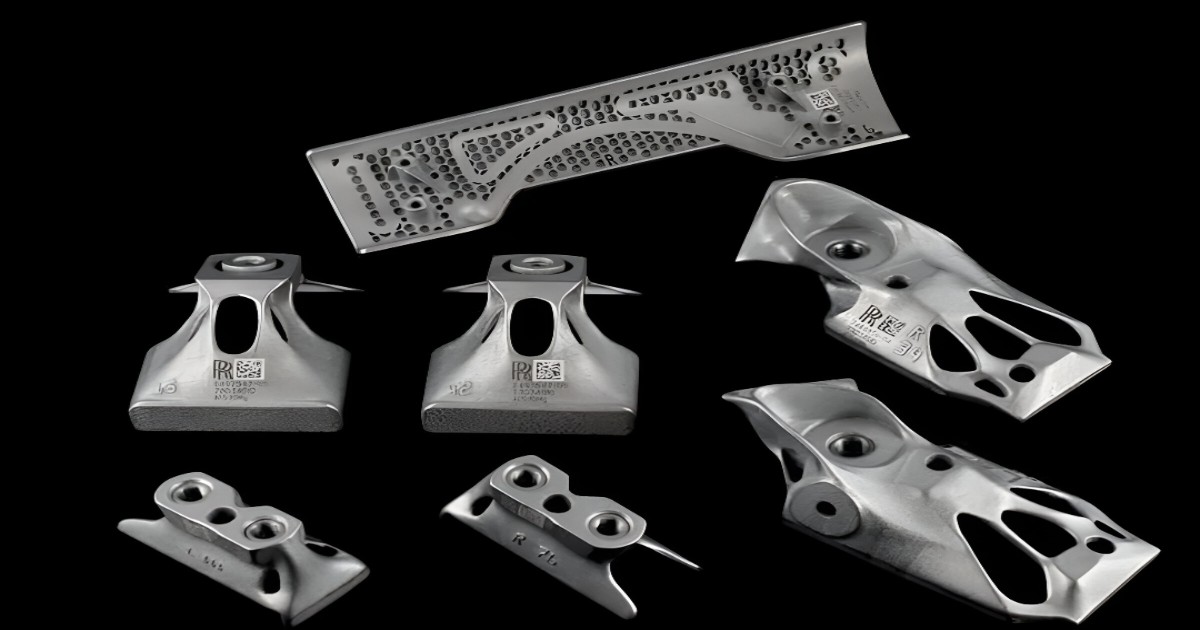

High-end luxury cars such as Porsche and Rolls Royce are utilizing this technology to shift all their physical inventories to digital. With the power of this machinery, these high-end car companies can produce spare parts demanded by their clients just as soon as the transportation of the spare part would take from the warehouse to the customer. Through this, companies are cutting down the requirement of warehouses as a whole.
A crucial advantage of 3D printing is also that it can be used to revive old cars by producing made-to-order spare parts based on individual cars. Another place where 3D printing is gaining momentum is in the area of competitive racing. Formula one race car companies such as McLaren and Renault are using this technique to produce parts that are usually very expensive and technical to produce using the traditional method. 3D printing allows engineers to use materials such as carbon fibers that improve the strength and speed of the car and also allow for more customization. The products produced by 3D printing are also much lighter but stronger, allowing more fuel efficiency and higher safety standards in the future.
While it may take a while before cars are completely made from 3D printing, there is a definite future in this technology, and with persistence, greater efficiency will be achieved.
With the situation we face today of COVID-19, the time for the development of the new product is scarce, as the product has to be tested and launched quickly in the market to counter the health situation today. The traditional method of manufacturing and testing the iterations seems to be against what is required today, as those methods are costlier, time-consuming, and difficult due to lockdown situations, which make it difficult for manufacturing molds, products, etc. The traditional method of manufacturing, like molding, requires molds to be produced for the different iterations to be tested, which is costlier and may take several days for the product to be manufactured and tested to check on product features and make changes for desirable results, and this long cycle goes on. The lockdown situation makes this process even worse with the unavailability of workers and stringent time factor we are fighting against.
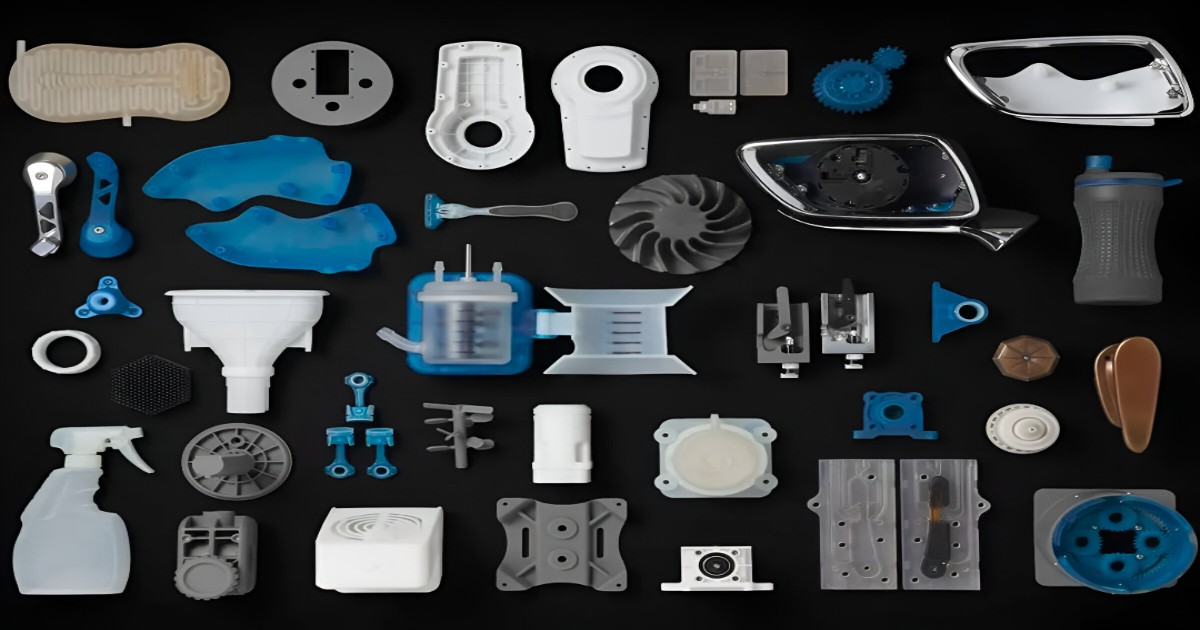

An effective prototype is one that can give product developers an accurate idea of how the final product will perform. Whether that is reviewing the texture and color or putting the part up to rigorous testing, engineers need a prototype that is up to the task. When it comes to product development, time is of the essence, especially if you had to put design iterations on hold during the lockdown. rapid prototyping is a blessing in disguise to counter the situation. Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using 3D CAD data. Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing or additive layer manufacturing technique. Your product development timeframe need not be affected by rapid prototyping at your service. Improving parts with 3D printing is quick, simple, and cheaper with many iterations that can be produced and tested as compared to traditional methods. In a few hours or a day, the original design can be updated on 3D CAD tools, and the file can be shared with the manufacturer digitally, and the prototype would be in your hands within a few hours or days, as per the complexity and size of the design. The manufacturing errors can easily be eliminated with rapid prototyping as compared to traditional methods of production. The models can easily be scaled as per the need, with limitations arriving only at the maximum size of product a given model of machine can produce. Cutting down on costs is a necessity for industries battling these tough times, but this, in essence, does not mean killing innovations necessary for progress.

Rapid prototyping enables innovation with its freedom of design for engineers to manufacture parts with intrinsic and small detailed designs and geometries with interlocking features, which is not possible to manufacture with traditional methods. This helps in creating product assemblies with many components into a single-component product, which in turn saves cost. Additive manufacturing offers huge varied combinations of technologies, from laser sintering to fused deposition modelling, and materials, from metals to plastics such as aluminium, nylon, and carbon fiber, that engineers can choose from to optimize their designs. It provides a variety of textures and colors to choose from. The input files can easily be changed to fulfill the design requirements.
© 2026 RA Global Tech Solutions
Site design and developed by Rajkar Global