The way technological advancement is reshaping the industries' design, innovation, and manufacturing, were reverse engineering has emerged as one of the most powerful tools driving industrial modernization with shrinking product lifecycles, growing demand for customization, and increasing pressure to deliver high-quality products, businesses across the globe.
A niche engineering practice has now evolved into an essential process for product development, 3D CAD modeling, motion analysis, stack-up analysis, design optimization, and innovation-driven redesign. As industries embrace 3D digitalization and reverse engineering, 3D scanning is playing a central role in bridging the gap between physical and digital worlds.
Let’s explore what reverse engineering is, its growing relevance in modern supply chains and how it is transforming various industrial sectors.
Reverse engineering is the process of capturing the physical geometry, features, and functional characteristics of an existing product to create a detailed 3D digital model. Instead of doing manual measurements, engineers start with using advanced technologies such as 3D laser scanning, profile projectors, CMM measuring mechanisms, point cloud processing, and surface reconstruction with parametric CAD modeling. These tools convert physical objects into highly accurate CAD models that can be used for optimization, redesign, remanufacturing, and quality validation.
At RA Global, we integrate advanced technology with deep engineering expertise to deliver exceptionally precise reverse engineering solutions. Our team converts complex physical components into Class A surface, editable, and manufacturable CAD models with high accuracy. RA Global offers reverse engineering services in Germany, Italy, Norway and Europe with superior accuracy results.
The growing importance of reverse engineering in most advanced and fast-moving technology is driven by challenges such as discontinued parts, long lead times, imported dependencies, and inconsistent quality. Reverse engineering offers an efficient solution by enabling companies to recreate obsolete or unavailable components, reduce dependability on overseas suppliers, improve accuracy in retrofitable part manufacturing, and maintain consistency across production batches. It also helps convert physical components into digital inventories while supporting localized manufacturing and faster turnaround times.
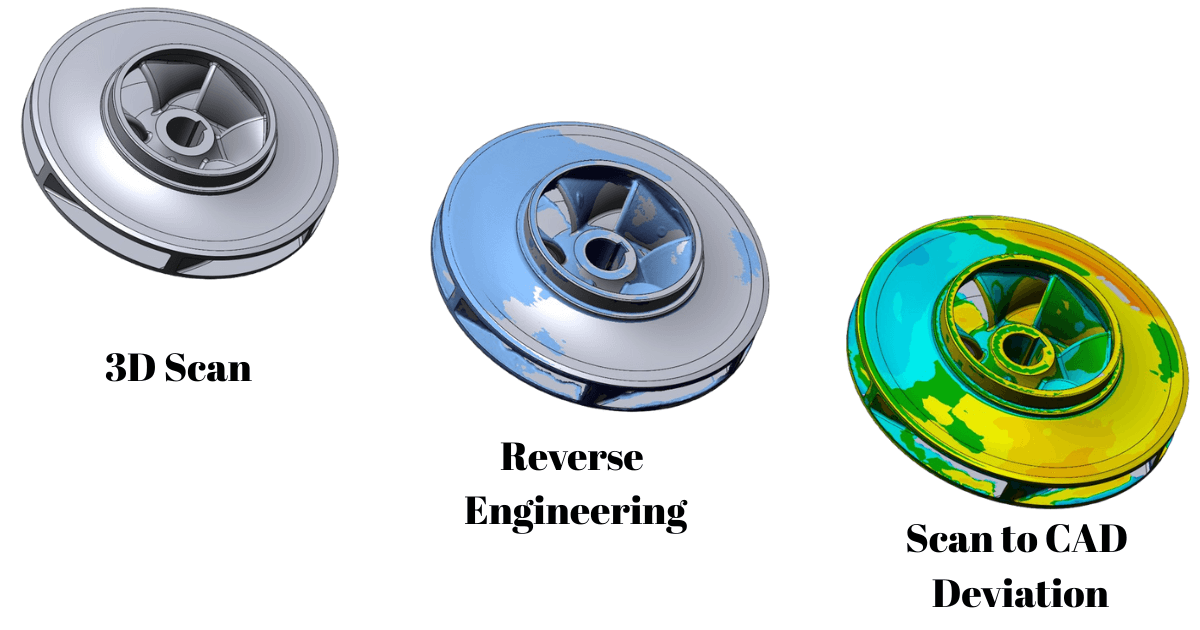
Reverse engineering has become indispensable across multiple industries due to its ability to enhance design accuracy, reduce costs, and revive legacy systems. Key industrial applications include:
Modern reverse engineering is all about precision, flexibility, and usability of the most advanced technologies. One of its standout features is high-accuracy 3D scanning, which can capture even the most intricate shapes, curves, and details of complex parts. Combined with point cloud and mesh processing, raw scan data is cleaned, aligned, and optimized, ready to be converted into 3D CAD design, parametric and surface CAD modeling. This data becomes fully editable CAD designs that can be used for redesign, manufacturing, or DFMEA. Beyond geometry, reverse engineering also provides insights into materials and manufacturing processes, helping engineers understand how a part was originally made. And the best part? These CAD models are fully compatible with CNC machining and 3D printing, making it easy to bring designs back to life in the real world.
Reverse engineering services bring a lot of advantages for modern industries. It allows companies to reproduce parts without original drawings, making it ideal for legacy conversion for lost or outdated documentation. By leveraging 3D scanning and digital modeling, reverse engineering accelerates product development, reduces design cycles, and speeds up prototyping. It also improves design efficiency by quick 3D CAD conversion, optimizing structures, enhancing performance, and minimizing material usage. Furthermore, reverse engineering offers cost-effective manufacturing, as digital rebuilding avoids expensive redesigns from scratch and repeatability of manufacturing to benchmark the product. Quality control is enhanced through precise comparison of scanned geometry with CAD models, ensuring dimensional accuracy. It also helps reduce lead times, enabling rapid part replacement and meeting deadlines for remanufacturing.
Reverse engineering is redefining how industries design, replicate, and optimize products. Whether it’s about replacing obsolete components, improving product performance, DFMEA, or supporting prototyping, reverse engineering has become a cornerstone of modern industrial innovation.
By speeding up the 3D CAD modelling and CAD conversion, reverse engineering empowers industries to unlock new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and competitiveness, making it an essential technology for the future.
The manufacturing sector is always changing, and 3D scanning technology is revolutionizing the field. The way businesses design, test, and manufacture products is being completely transformed by 3D scanners, which can improve quality control and Product Development. With its precision, speed, and flexibility, this technology is revolutionizing manufacturing processes in a variety of industries, including consumer goods, automotive, medical devices, and aerospace.
A 3D scanner measures an object's geometry using lasers, structured light to create a digital model of the object's physical dimensions. In industries where accuracy is crucial, this comprehensive 3D representation is a useful tool because it can be examined, altered, or replicated in a variety of ways.
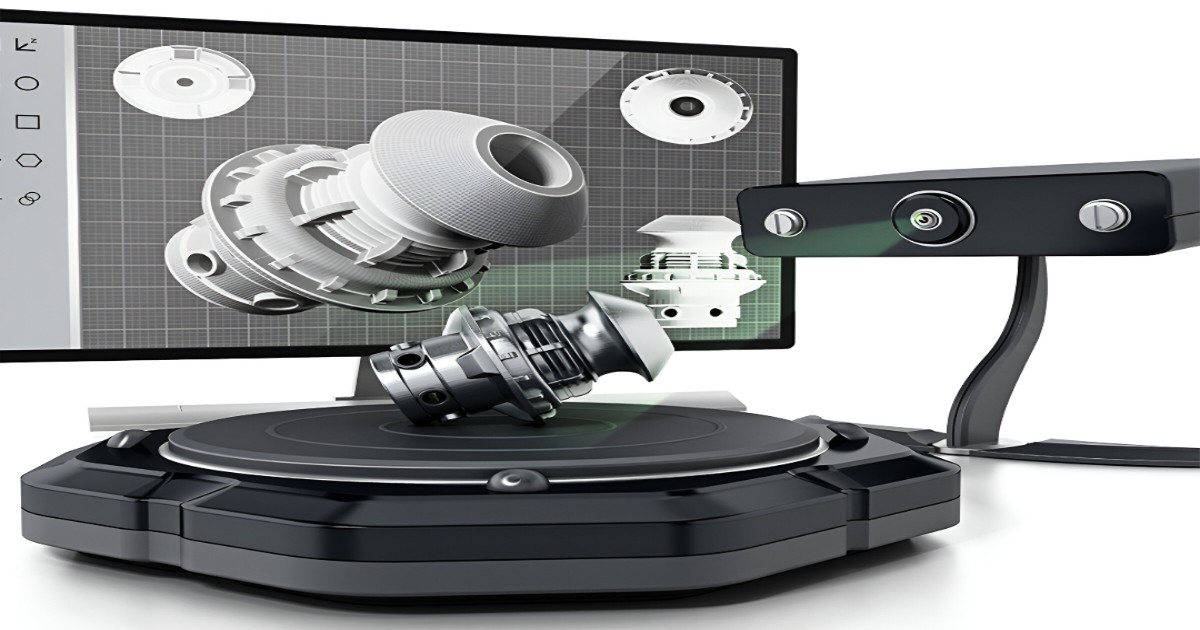

Laser scanners: Use laser beams to capture the surface details of an object.
Structured light scanners: Project light patterns onto an object and capture its shape based on distortions in the light pattern.
Photogrammetry scanners: Use photos from multiple angles to construct a 3D model.
Development and prototyping of products: One of the most important uses for 3D scanners in manufacturing is product development. In traditional manufacturing, creating a prototype can be time-consuming and costly. With 3D scanning, companies can quickly capture existing parts or objects, modify them digitally, and create rapid prototypes using 3D printing or other techniques. Faster iterations during product development are made possible by this, which also speeds up the design-to-production cycle.
Reverse Engineering: Reverse Engineering allows manufacturers to take a physical product, scan it, and generate accurate 3D models to replicate or improve upon. This process is invaluable for: Legacy parts: When original designs are lost or no longer available. Custom parts: Manufacturers can create bespoke or customized components without needing original CAD models.
Competitor Analysis: By scanning competitor products, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement in their own designs.
Quality Control and Inspection: Quality control is critical in manufacturing, where even minor deviations can lead to product failure or costly recalls. 3D scanners help manufacturers perform detailed quality inspections by comparing scanned parts to their original CAD Designs, ensuring they meet exact specifications. The high precision of 3D scanning makes it easy to identify defects, warping, or deviations in real time, reducing waste and minimizing costly production errors.
Increased Accuracy and Precision: The incredibly high accuracy of 3D scanning technology—often within microns—makes it perfect for sectors like aerospace and automotive manufacturing that demand precise specifications. The ability to capture fine details reduces errors and inconsistencies and guarantees that the finished product matches the digital model exactly.
Faster Production Times: 3D scanners shorten the time needed to launch a product by expediting the design and inspection stages. Businesses are able to produce prototypes, carry out quality assurance procedures, and make design modifications more quickly. This enables producers to remain ahead of the competition and respond to market demands more quickly.
Cost Savings: While investing in 3D scanners may seem like a large upfront cost, the technology ultimately saves manufacturers money. By identifying design flaws early in the process and reducing material waste, companies can minimize production costs. Additionally, fewer errors mean fewer resources spent on rework or corrections.
Improved Customization: Customization is becoming a significant trend in modern manufacturing. Whether for medical devices tailored to a patient’s anatomy or custom automotive parts, 3D scanners allow for rapid and accurate customization. Scanning a unique object or human body part can provide precise data that is essential for producing a perfect fit, which is particularly useful in industries such as healthcare and fashion.

Aerospace: The aerospace industry demands exacting standards of precision and quality. 3D scanners are used for reverse engineering older parts, creating new designs, and conducting quality inspections. They allow aerospace companies to maintain high standards while reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Automotive: In automotive manufacturing, 3D scanners are used to design, inspect, and reverse engineer parts and components. The technology enables manufacturers to reduce prototyping times and improve vehicle safety by ensuring parts meet stringent quality standards.
Healthcare: In the medical field, 3D Scanning is being used to make surgical implants, dental appliances, and custom prosthetics. Analyzing a patient's anatomy enables highly customized devices and treatments, which enhance patient outcomes.
With the advancement and accessibility of 3D scanning technology, its use in manufacturing is only expected to increase. In the future, we can expect:
Integration with AI: Artificial intelligence can help analyze 3D scan data more efficiently, identifying potential issues or areas for improvement.
Real-time scanning: Faster processing speeds will enable real-time scanning and analysis, further speeding up production workflows.
Improved affordability: As the technology matures, the cost of 3D scanners will continue to decrease, making it accessible for businesses of all sizes.
By increasing accuracy, decreasing production times, and lowering costs, 3D scanners are transforming the manufacturing industry. A competitive edge can be gained by incorporating 3D scanning technology into your workflow, regardless of how big or small your business is. If you are prepared to embrace the manufacturing of the future, you might want to invest in 3D scanners to streamline your quality control, design, and prototyping procedures. The result? Faster production, higher quality products, and increased customer satisfaction.
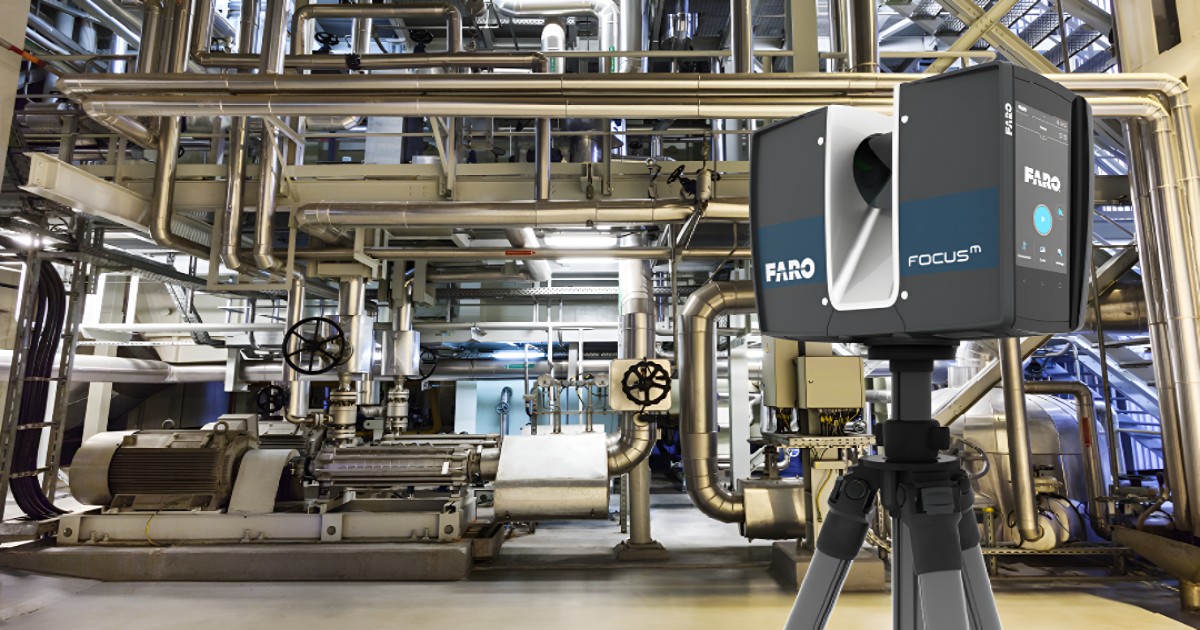
3D laser scanning technology has completely changed how industries collect, analyze, and interpret physical data. Whether it is applied to engineering, manufacturing, construction, or even preservation, 3D laser scanning provides unmatched accuracy and efficiency when mapping intricate geometries. As industries increasingly adopt this advanced technology, it's clear that 3D laser scanning is becoming a key tool for many professionals worldwide.
At its core, 3D laser scanning is a process that uses 3D lasers to capture a physical object’s shape, dimensions, and spatial orientation in high detail. The technology works by emitting a 3D laser source onto an object and measuring the reflection to generate thousands or even millions of precise data points. These points are then compiled to create a point cloud, which is a highly accurate digital representation of the 3D scanned object or environment.

Precision and preciseness: The great accuracy offered by 3D laser scanning is among its most important benefits. Human error is frequently a possibility with traditional methods of mapping and measuring objects, but 3D laser scanning removes this issue. Even the smallest details can be captured by the technology, guaranteeing accurate measurements that are crucial for projects that need precise specifications.
Efficiency in data collection: 3D laser scanning is incredibly efficient when it comes to collecting large amounts of data in a short time. In industries where time is of the essence, such as industrial design and construction, this is particularly helpful. As opposed to the hours or days that manual measurement typically takes, it can be finished in a fraction of the time without compromising accuracy.
Architecture and construction: Used for designing blueprints or retrofitting projects.
Manufacturing: Helps in reverse engineering parts or ensuring product quality.
Cultural heritage: For preserving historical monuments and artifacts.
Healthcare: Assists in creating custom prosthetics or anatomical models.
3D Scanning the object or environment: The 3D laser scanner is set up at a fixed location. After that, it starts to shoot laser beams that move over the target object. A data point is gathered each time the laser strikes a surface, depending on the angle and distance of the reflection.
Creating a point cloud: As the 3D scanner moves, it gathers millions of these points, creating a point cloud. This cloud forms a highly detailed, three-dimensional digital model of the 3D scanned object or environment.
Post-processing and analysis: Once the point cloud is generated, it is transferred to specialized software where it can be manipulated for various uses. Engineers, architects, or designers can then analyze the model for any necessary modifications or measurements.
Construction and architecture: In construction, 3D laser scanning is a valuable tool for designing and planning structures. It can swiftly map out expansive spaces or existing structures, giving construction teams access to extremely precise data. Errors are decreased, and improved project management is made possible.
Manufacturing and reverse engineering: 3D laser scanning plays a pivotal role in reverse engineering. By 3D scanning existing parts or prototypes, manufacturers can recreate designs, perform quality checks, or improve upon existing products. This is essential for industries like automotive or aerospace, where precision is key.
Preservation and restoration: For museums and cultural institutions, 3D laser scanning is an excellent tool for preserving historical artifacts. It allows for detailed replication and conservation of ancient buildings or sculptures, ensuring that cultural heritage is maintained for future generations.
In terms of accuracy, speed, and versatility, 3D laser scanning is simply superior to conventional measurement techniques like tape measures and digital calipers, which have been in use for centuries. Laser scanning is the more effective and dependable option for complex projects because it can collect data from hard-to-reach places and is less likely to make mistakes.
As technology evolves, 3D laser scanning is only expected to become more advanced. Innovations such as faster scanning times, improved portability, and integration with other technologies like artificial intelligence or augmented reality will likely make this technology even more indispensable across various industries.
In conclusion, 3D laser scanning is a useful tool in sectors like manufacturing, cultural preservation, and construction because of its many advantages. It is a worthwhile investment for businesses trying to streamline their operations and lower human error because of its quick turnaround time and capacity to provide accurate, comprehensive data.
If you want to use innovative techniques for your projects, think about utilizing 3D laser scanning to reach new levels of accuracy and productivity.
© 2026 RA Global Tech Solutions
Site design and developed by Rajkar Global