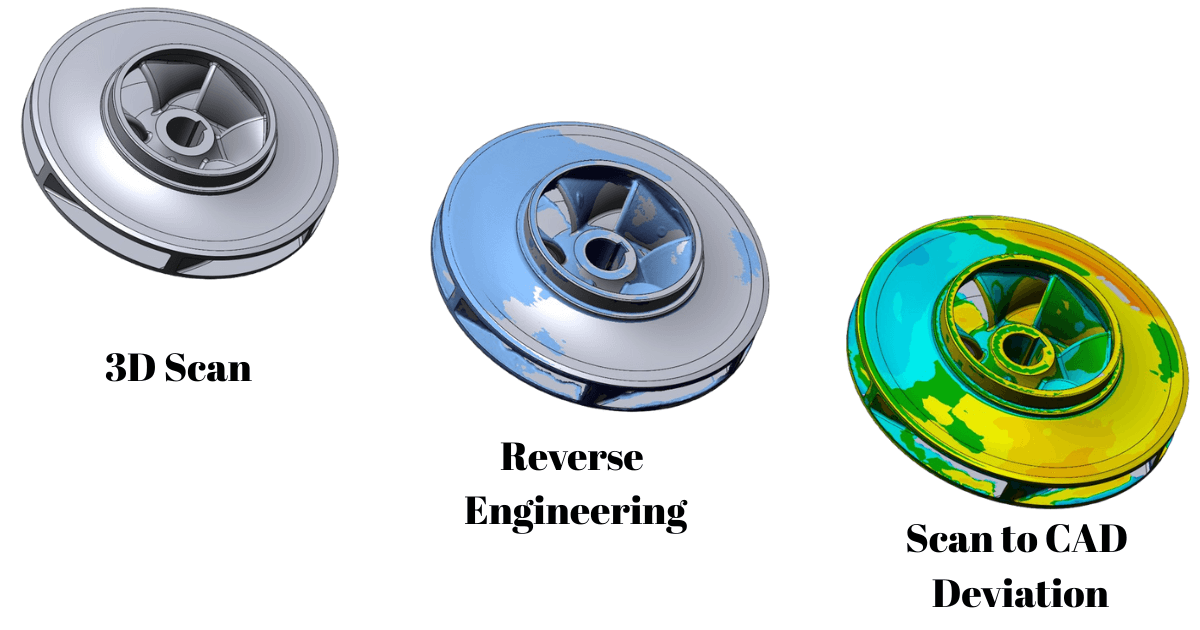
3D scanning and reverse engineering are powerful technologies that help capture, analyze, and reproduce physical objects with precision. Depending on the project requirements and end applications, these processes offer a range of deliverables, from accurate digital 3D models and point clouds to CAD designs ready for manufacturing. In this blog, we will explore the various key deliverables of 3D scanning and reverse engineering with their use cases.
Point cloud data is a raw digital output composed of millions of discrete points in three-dimensional space, with each point defined by its X, Y, and Z coordinates. Together, these points accurately map the surface geometry of a scanned object, capturing its shape and structural details with high precision. Modern laser scanners and LIDAR systems are capable of collecting tens of millions of points in a single scan, enabling the accurate representation of even highly complex and freeform geometries.

Mesh models are generated by converting point cloud data into a surface mesh composed of triangles or other polygonal elements. They provide a clear and visually coherent representation of an object’s surface geometry and are widely used for visualization, analysis, and 3D printing applications. While mesh models accurately capture external surface details, they are not ideal for direct design modifications or conventional manufacturing processes, as they lack parametric and feature-based information.
Editing mesh models can be complex and typically requires specialized sculpting or reverse engineering tools such as Geomagic Freeform or other digital sculpting software. These tools enable users to modify organic shapes, refine surface details, and prepare mesh models for further manufacturing workflows. Mesh models are most commonly exported in .STL format, which is the industry-standard file format for 3D printing. Our 3D scanners are capable of directly delivering mesh models in .STL format, eliminating the need for intermediate processing and enabling faster downstream workflows.

When an object is 3D scanned using color-capable 3D scanners such as Einscan, FARO 3D, or other scanners that can capture color information, mesh models can be delivered with realistic texture and color data. These scanners record not only the shape of the object but also its surface colors, resulting in textured mesh models that closely match the real-world appearance. Such textured mesh models can be exported in file formats that support color and texture information, making them suitable for visualization, presentation, and creative applications.
Reverse-engineered CAD models help connect design and manufacturing by allowing CAD data to be directly used in CAM software. This makes the production process faster and smoother. These models also help improve design work by converting “dumb” or non-editable solids into fully editable CAD models, giving engineers better control over the design. Reverse-engineered CAD data is commonly used to create accurate tools, dies, and molds, which helps speed up the manufacturing of complex parts. It is also useful for checking packaging and assembly fit, ensuring that products fit correctly within given space limits.
These CAD models can be imported into CAE software for simulations and analysis, helping engineers improve product strength, performance, and reliability. Reverse-engineered CAD models are widely used in 3D printing to create physical prototypes and functional parts. They also make it easier to modify, improve, or upgrade existing designs without starting from scratch. By adjusting these models, companies can create customized products based on specific needs. In addition, reverse engineering helps generate CAD models of existing parts for maintenance and aftermarket production. These models also support better teamwork by providing a common reference that design, engineering, and manufacturing teams can easily understand and use.

At RA Global, 3D scanning and reverse engineering are more than just technologies; we are practical solutions that help industries digitize, analyze, and optimize real-world assets with accuracy and efficiency. By delivering a complete range of outputs, including point cloud data, mesh models (with or without color textures), and fully reverse-engineered CAD models, RA Global supports every stage of the product and asset lifecycle.
Our expertise enables manufacturers to recreate legacy parts, improve existing designs, and move seamlessly from physical components to production-ready CAD models. From factory CAD modeling and scan-to-BIM solutions to precision inspection, simulation-ready CAD, and 3D printing support, RA Global ensures that each deliverable is tailored to your project requirements and end applications. Whether it is manufacturing, infrastructure, cultural heritage, geospatial analysis, or product development, our advanced 3D scanning and reverse engineering services help reduce time, minimize errors, and improve decision-making. By combining advanced scanning technologies with skilled engineering expertise, RA Global delivers reliable, accurate, and industry-ready digital solutions that empower organizations to innovate faster, maintain quality, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
The way technological advancement is reshaping the industries' design, innovation, and manufacturing, were reverse engineering has emerged as one of the most powerful tools driving industrial modernization with shrinking product lifecycles, growing demand for customization, and increasing pressure to deliver high-quality products, businesses across the globe.
A niche engineering practice has now evolved into an essential process for product development, 3D CAD modeling, motion analysis, stack-up analysis, design optimization, and innovation-driven redesign. As industries embrace 3D digitalization and reverse engineering, 3D scanning is playing a central role in bridging the gap between physical and digital worlds.
Let’s explore what reverse engineering is, its growing relevance in modern supply chains and how it is transforming various industrial sectors.
Reverse engineering is the process of capturing the physical geometry, features, and functional characteristics of an existing product to create a detailed 3D digital model. Instead of doing manual measurements, engineers start with using advanced technologies such as 3D laser scanning, profile projectors, CMM measuring mechanisms, point cloud processing, and surface reconstruction with parametric CAD modeling. These tools convert physical objects into highly accurate CAD models that can be used for optimization, redesign, remanufacturing, and quality validation.
At RA Global, we integrate advanced technology with deep engineering expertise to deliver exceptionally precise reverse engineering solutions. Our team converts complex physical components into Class A surface, editable, and manufacturable CAD models with high accuracy. RA Global offers reverse engineering services in Germany, Italy, Norway and Europe with superior accuracy results.
The growing importance of reverse engineering in most advanced and fast-moving technology is driven by challenges such as discontinued parts, long lead times, imported dependencies, and inconsistent quality. Reverse engineering offers an efficient solution by enabling companies to recreate obsolete or unavailable components, reduce dependability on overseas suppliers, improve accuracy in retrofitable part manufacturing, and maintain consistency across production batches. It also helps convert physical components into digital inventories while supporting localized manufacturing and faster turnaround times.
Reverse engineering has become indispensable across multiple industries due to its ability to enhance design accuracy, reduce costs, and revive legacy systems. Key industrial applications include:
Modern reverse engineering is all about precision, flexibility, and usability of the most advanced technologies. One of its standout features is high-accuracy 3D scanning, which can capture even the most intricate shapes, curves, and details of complex parts. Combined with point cloud and mesh processing, raw scan data is cleaned, aligned, and optimized, ready to be converted into 3D CAD design, parametric and surface CAD modeling. This data becomes fully editable CAD designs that can be used for redesign, manufacturing, or DFMEA. Beyond geometry, reverse engineering also provides insights into materials and manufacturing processes, helping engineers understand how a part was originally made. And the best part? These CAD models are fully compatible with CNC machining and 3D printing, making it easy to bring designs back to life in the real world.
Reverse engineering services bring a lot of advantages for modern industries. It allows companies to reproduce parts without original drawings, making it ideal for legacy conversion for lost or outdated documentation. By leveraging 3D scanning and digital modeling, reverse engineering accelerates product development, reduces design cycles, and speeds up prototyping. It also improves design efficiency by quick 3D CAD conversion, optimizing structures, enhancing performance, and minimizing material usage. Furthermore, reverse engineering offers cost-effective manufacturing, as digital rebuilding avoids expensive redesigns from scratch and repeatability of manufacturing to benchmark the product. Quality control is enhanced through precise comparison of scanned geometry with CAD models, ensuring dimensional accuracy. It also helps reduce lead times, enabling rapid part replacement and meeting deadlines for remanufacturing.
Reverse engineering is redefining how industries design, replicate, and optimize products. Whether it’s about replacing obsolete components, improving product performance, DFMEA, or supporting prototyping, reverse engineering has become a cornerstone of modern industrial innovation.
By speeding up the 3D CAD modelling and CAD conversion, reverse engineering empowers industries to unlock new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and competitiveness, making it an essential technology for the future.
India's maritime strength is entering a transformative phase. The Indian Navy has adopted three powerful mantras—Indigenization, Innovation, and Integration to shape its journey toward a fully Aatmanirbhar future by 2047. This bold initiative marks a strategic shift from dependence to dominance, positioning Indian industry at the heart of next-generation naval warfare development.
Indigenization is more than a policy; it's a national commitment. The Indian Navy is ensuring that the majority of its ships, systems, and components are designed and built within the country. Out of 65 ships under construction, 63 are being built at Indian shipyards, symbolizing a true Builder’s Navy.
It is a matter of immense pride for us as a nation that India is one of only six countries in the world capable of designing, building, and operating both aircraft carriers and nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs). This remarkable achievement stands as a testament to India’s growing technological maturity, industrial capability, and strategic foresight.
This milestone represents not just a capability, but a mindset one where Indian engineering firms, R&D units, and technology partners are driving home-grown innovation. By promoting local manufacturing of critical systems like propulsion units, sensors, and weapon systems, the Navy is reducing its import dependence and strengthening India’s industrial base.

Innovation is deeply embedded in the Indian Navy's DNA. As author Steven Johnson notes in his book Where Good Ideas Come From, innovation does not come from giving incentives; it comes from creating environments where ideas can connect.
This philosophy perfectly mirrors the Navy's approach to building a culture of creativity and collaboration. Recognizing that innovation thrives in connected ecosystems, the Indian Navy established the Naval Innovation and Indigenisation Organisation (NIIO) in 2021. The NIIO acts as a catalyst linking industry, academia, startups, and research institutions to transform bold ideas into deployable technologies for the defense ecosystem.
Through initiatives like iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) and NIIO, the Navy has been actively nurturing an environment where innovation is continuous, practical, and mission-driven. These initiatives are accelerating the adoption of breakthrough technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, autonomous systems, and additive manufacturing, all of which are redefining the future of naval warfare.
The third mantra Integration represents the Indian Navy’s holistic approach to modern warfare and technological advancement. Integration is not only about combining hardware and software systems; it’s about connecting people, processes, and purpose to achieve strategic synergy.
The Navy’s emphasis on integration ensures that advanced platforms such as ships, submarines, aircraft, sensors, and communication networks operate as a unified force. This seamless interoperability is essential for network-centric operations, where real-time data exchange and synchronized decision-making determine mission success.
Integration also extends beyond systems; it involves bringing together industry, academia, and research institutions under one cohesive framework. Through collaborative programs with DRDO, DPSUs, MSMEs, and private technology firms, the Navy has built an ecosystem that ensures technological innovation flows smoothly from concept to deployment. This partnership-driven approach enhances agility, reduces development cycles, and ensures that the latest indigenous technologies are rapidly integrated into frontline operations.

The establishment of platforms like the Technology Development Acceleration Cell (TDAC) and the Naval Design Bureau (NDB) highlights the Navy’s vision of institutional integration, where design, testing, production, and deployment work hand in hand. This integrated structure ensures that the Navy remains future-ready, adaptable, and self-reliant in the face of evolving maritime challenges.
At RA Global Tech Solutions, this vision deeply resonates with our mission of driving engineering innovation, design excellence, and technological independence through advanced engineering design services, 3D scanning, reverse engineering, and product development. As India’s defense and maritime sectors evolve, the synergy between industry and the armed forces has never been more vital. Our precision engineering and manufacturing support services echo this very principle. From casting and forging to digital design validation and reverse engineering, we enable industries to replicate, refine, and reinvent components with world-class accuracy essential for achieving true indigenization.
Our work in 3D laser scanning, CAD modeling, and rapid prototyping empowers defense and manufacturing clients to visualize, simulate, and perfect their designs with exceptional accuracy. By combining creativity with technology, we help bridge the gap between conceptual design and production reality. We practice this same philosophy through our end-to-end service ecosystem, integrating product design, analysis, prototyping, and testing under one roof. Our solutions are designed to align with the broader vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat, ensuring that technology and talent come together for maximum impact.
Our collaboration-centric approach and advanced technology capabilities make RA Global a trusted partner for industries contributing to India’s strategic growth, from marine engineering to aerospace and heavy manufacturing.
As India moves toward its goal of becoming a fully Aatmanirbhar defense power by 2047, collaboration between the Navy and Indian industry will define the success of this journey. The three mantras, Indigenization, Innovation, and Integration, are not just guiding principles; they represent a roadmap to a stronger, smarter, and more secure India.
RA Global Tech Solutions stands committed to being part of this transformation, delivering engineering solutions that reflect the precision, integrity, and innovation the Indian Navy itself embodies.
The Indian manufacturing sector is undergoing a massive transformation, powered by government policies, digital innovation, and rising global demand. With initiatives like Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, the country is steadily becoming a global manufacturing hub.
In this article, we highlight the top 10 fastest-growing manufacturing sectors in India for 2025 that showcase how these industries are shaping the future.
The Indian EV market is witnessing explosive growth, with EV component exports reaching $23 billion in FY25. Backed by FAME-II and PLI auto schemes, this sector is shaping the future of sustainable mobility.
Tata Motors Nexon EV has become one of India’s most popular electric vehicles, showcasing strong consumer adoption.

Electronics is one of India's fastest-growing industries, valued at $115 billion in 2024 and expected to triple by 2026. The ₹76,000 crore Semicon India Programme is driving investments in semiconductor fabs, chip design, and electronic product manufacturing.
Samsung’s Noida factory, one of the world’s largest mobile manufacturing plants, produces smartphones and consumer electronics for domestic and global markets.
India aims to reach 300 million tonnes of steel production by 2030. Smart automation, predictive maintenance, and AI-powered quality control are reshaping the metals industry.
Tata Steel’s Jamshedpur and Kalinganagar plants lead with state-of-the-art automation and sustainable production practices.

India remains the pharmacy of the world, exporting $25+ billion worth of drugs in 2024. With IoT-enabled cold chain logistics and precision drug delivery systems, biotech and pharma manufacturing are embracing Industry 4.0.
Sun Pharma's advanced facilities produce generics, specialty medicines, and complex formulations for global markets.

Projected to hit $23 billion by 2030, India’s drone sector is becoming crucial for defense, agriculture, surveillance, and logistics.
ideaForge, a pioneer in drone manufacturing, supplies UAVs for mapping, defense, and inspection applications.

India's data center industry surpassed $5 billion in 2024, growing at 25% CAGR. Rising demand for AI, IoT, and cloud services is fueling large-scale investments in digital infrastructure.
Sify Technologies operates modern data centers across India, supporting enterprises with scalable cloud and IT services.

The embedded systems market, valued at $4.47 billion in 2024 with a CAGR of 10.3%, powers robotics, PLCs, and smart factories. Industrial automation is helping manufacturers improve productivity, reduce errors, and cut costs.
Bosch India leverages advanced automation and embedded platforms for automotive and industrial component production.
Technical textiles are gaining momentum in sectors like defense, sports, healthcare, and agriculture. Innovations such as RFID integration, antimicrobial fabrics, and biosensor-embedded wearables are fueling growth.
SRF Limited produces high-performance technical textiles for industrial and defense applications.

India is benefiting from the global China+1 strategy, emerging as a reliable supplier of specialty chemicals used in agriculture, pharma, and construction. Automation ensures safe, efficient, and scalable chemical production.
Meghmani Finechem and Hikal are expanding their specialty chemical facilities to meet global demand.

The Indian medical device industry is rapidly expanding, driven by Make in India policies and rising healthcare needs. Portable diagnostics, wearable monitors, and affordable surgical tools are in high demand.
HLL Lifecare, a government-owned firm, manufactures medical devices ranging from diagnostic tools to surgical consumables.
RA Global brings precision and innovation to industries with its comprehensive suite of 3D scanning, reverse engineering, and product design services. By combining cutting-edge technology with expert knowledge, we empower businesses to transform their products and processes. From product development and prototyping to production and quality control, RA Global and its solutions help clients achieve accuracy, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. With a focus on delivering high-quality products, we support companies across manufacturing, automotive, construction, consumer products, drones, aerospace and defense, electric vehicles, general engineering and manufacturing, healthcare and medical devices, oil and gas, robotics and automation, and textiles plant and machinery, driving growth and success in an ever-evolving landscape.
As India's manufacturing sector continues to evolve, driven by government initiatives, digital innovation, and global demand, RA Global is at the forefront of this transformation. With its cutting-edge 3D scanning, reverse engineering, and product design services, RA Global is empowering businesses across the top 10 fastest-growing manufacturing sectors in India to achieve precision, efficiency, and success. By leveraging technology and expertise, RA Global is helping companies drive growth, innovation, and competitiveness in an ever-evolving landscape. Whether you are a startup or an established player, partner with RA Global to unlock new opportunities and shape the future of manufacturing in India.
In the fast-paced world of technology, innovation and vision are the driving forces behind successful companies. RA Global Tech is one such company that has turned its vision into reality, providing cutting-edge technology solutions to businesses worldwide. Let us take a closer look at the story of RA Global Tech Solutions LLP and how it has evolved from an idea to a thriving technology company.

In 2017, RA Global Tech Solutions embarked on a remarkable journey, fueled by a vision to bridge the gap between technology and innovation. From a small office space with just one PC, the company has grown into a trusted partner for businesses across various industries.
With a team of passionate and experienced engineering professionals, RA Global began its quest to deliver tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of its clients. From concept to commissioning, the team ensured seamless execution and exceptional quality, laying the foundation for long-term partnerships with clients.
As the company grew, so did its expertise. The RA Global team expanded, and its capabilities evolved to include
Through its journey, RA Global has remained committed to delivering value to its clients. By fostering strong partnerships and providing exceptional solutions, the company has established itself as a leader in the engineering services industry.

By partnering with RA Global, businesses can unlock the potential of trusted engineering solutions and services, transforming ideas into tangible successes.
Driven by a relentless pursuit of engineering excellence, RA Global Tech Solutions operates as a trusted partner to some of the world's most influential brands across multiple industries, including automotive, aerospace and defense, medtech and healthcare, energy, and more. At the heart of RA Global's approach is a conviction that true engineering transformation comes from partnership. Rather than offering transactional support, the company embeds engineering teams inside client ecosystems through what it calls Virtual Business Units (VBUs). These dedicated teams are empowered to make decisions at speed, collaborate across time zones, and co-create custom solutions at the source of the client need. Whether designing innovative product solutions, optimizing complex systems, or building predictive models, RA Global delivers full lifecycle engineering solutions. With expertise spanning various domains, RA Global is committed to driving engineering excellence and delivering value to its clients. By partnering with RA Global, businesses can unlock the potential of trusted manufacturing solutions and services, transforming ideas into tangible successes.
Our journey began with a vision to bridge the gap between technology and innovation. We have worked tirelessly to make that vision a reality, delivering high-end engineering services that drive innovation and growth. With a team of experienced engineers and experts, we have provided tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of our clients. Our mission is to empower businesses with cutting-edge engineering solutions that enhance their competitiveness, efficiency, and sustainability. We strive to deliver exceptional value to our clients, partners, and stakeholders through our expertise, creativity, and commitment to excellence. At RA Global Tech Solutions, we are dedicated to delivering innovative engineering solutions that drive growth and excellence. With our expertise, commitment to quality, and customer-centric approach, we are confident that we can help businesses achieve their goals.
The transportation industry is on the cusp of a revolution, with electric cars and planes leading the charge. As the world shifts towards sustainable transportation, electric propulsion systems, advanced battery technology, and lightweight materials are playing a crucial role in shaping the future of transportation.
Electric transportation offers several benefits, including

Several key technologies are driving the development of electric aviation and cars, including:
Norway, a country known for its commitment to clean living and sustainable transportation, is now turning its attention to electric planes. With one of the largest Tesla markets in the world, Norway has already demonstrated its dedication to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Now, it's taking the next step by exploring electric aviation. Norway is making significant strides in electric aviation, showcasing its commitment to reducing emissions and connecting remote communities. The Alia CX300, a fully electric aircraft developed by Beta Technologies, recently completed a test flight from Stavanger to Bergen, marking a major milestone in Norway's electric aviation ambitions.
To achieve decarbonization in aviation, various technologies are crucial. Key among these are innovative propulsion methods like electrification, hybrid power, and hydrogen fuel cells. At Airbus, we're researching electrification to pave the way for industry adoption and regulatory approval of alternative propulsion for aircraft, helicopters, and urban air vehicles.
Hybrid-electric propulsion is set to transform the aviation industry by combining multiple energy sources to optimize energy efficiency and reduce fuel consumption. This innovative technology offers several key advantages, including fuel savings of up to 5% compared to traditional flights, enhanced efficiency through optimized energy management, and a more sustainable future for aviation through reduced greenhouse gas emissions.

At RA Global, we are committed to contributing our expertise in 3D scanning, reverse engineering, and CAD design to help shape the future of electric aviation and cars. Our services include:
While electric aviation and cars hold great promise, there are still challenges to overcome, including:
The future of transportation is electric, and at RA Global, we are excited to contribute to this innovation. With electric propulsion systems, advanced battery technology, and lightweight materials shaping the future of transportation, we're paving the way for a cleaner, quieter, and more efficient transportation industry.
In recent years, 3D Printing has emerged as a transformative force in various sectors around the globe, and India is no exception. India's 3D printing industry is gaining traction, transitioning from prototype-focused applications to end-product manufacturing, driven by reduced costs and accelerated by AI integration.
Agnikul, a Chennai-based spacetech firm, made history with the world's first rocket launch powered by a single-piece 3D-printed engine. What's remarkable is that they achieved this feat in just three days, a significant reduction from the typical 10-11 months of preparation time, where manufacturing a rocket engine alone usually takes six months. This innovation greatly cut down time, effort, and costs.
India's 3D printing market is gaining momentum, with diverse applications emerging across industries. According to IMARC Group, the Indian 3D printing market, valued at $707 million in 2024, is projected to reach $4.3 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 21.7%.
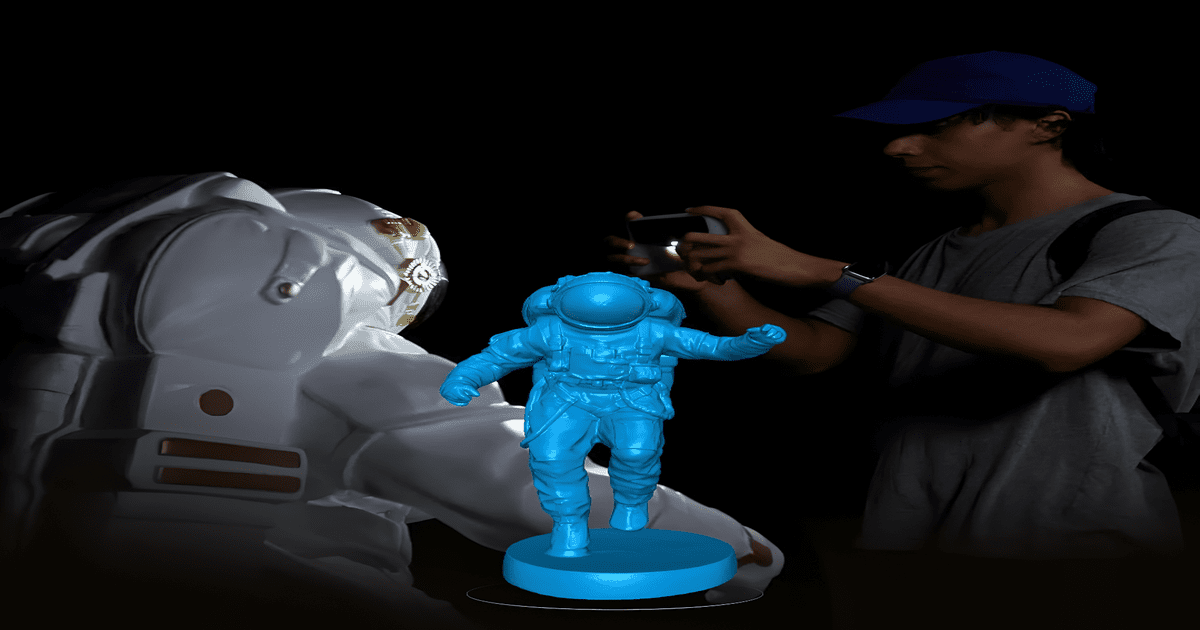

The toy industry is another area where 3D printing is making waves, allowing for designs that were previously impossible or prohibitively expensive to produce. Customizable toys that reflect the preferences of individual consumers are becoming increasingly popular, thanks to this technology. For example, parents can now design toys tailored to their children’s interests, which adds personal value to the products.
This shift toward customization is not only enhancing consumer satisfaction but also promoting a culture of creativity and innovation among young creators and entrepreneurs in India.
RA Global offers various services that can support the implementation of Rocket Fuel to Playful Tools, including
Despite the exciting developments, challenges remain. One significant hurdle is the need for skilled labor capable of operating advanced 3D printing technologies and software. Therefore, educational institutions and industry must collaborate to develop specialized training programs to build a proficient workforce.
Furthermore, regulatory frameworks need to evolve to address intellectual property issues associated with 3D printing. As the technology becomes mainstream, safeguarding innovation while fostering collaboration will be essential for sustained growth.
The 3D printing industry is shifting towards more sustainable raw materials, moving beyond traditional plastics and polymers to eco-friendly options like biodegradable cornstarch. This global trend towards environmentally responsible alternatives is being actively adopted in India.
3D printing is poised to be a catalyst for India’s industrial renaissance, fundamentally changing the way products are designed and manufactured across numerous sectors. From aerospace to consumer goods, the applications of this technology are vast and varied.
As we embrace these advancements, India stands at the threshold of a manufacturing revolution—one that has the potential to stimulate economic growth, encourage entrepreneurship, and position the country as a leader in the global market. The possibilities are limitless, and as 3D printing continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of Indian industry.
In the era of Industry 4.0, precision and digital integration are no longer optional; they are the foundation of competitiveness. Engineering and manufacturing sectors are shifting toward data-driven workflows where the line between the physical and digital is seamless. At the heart of this transformation lie 3D scanning and reverse engineering, two domains in which RA Global has established strong expertise.
Technical Foundations of 3D Scanning
3D scanning technologies convert real-world geometries into accurate digital point clouds. Depending on application and accuracy requirements, RA Global deploys:
The resulting point clouds are processed into polygon meshes and then into parametric CAD models. This workflow ensures not only high-fidelity reproduction of geometry but also a solid foundation for simulation, modification, or manufacturing.
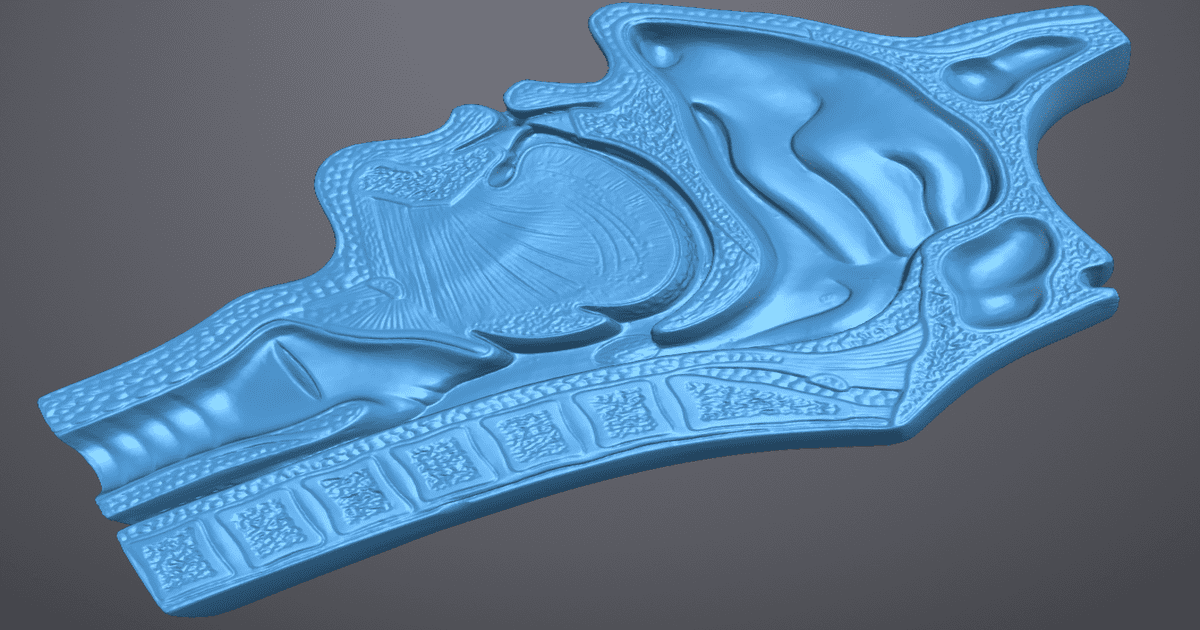
Reverse engineering goes beyond digitization; it creates usable design intelligence from physical objects. RA Global applies a structured workflow:
RA Global is a leading mechanical engineering company in Mumbai, providing advanced 3D scanning, reverse engineering, and 3D CAD design services as the technical backbone of modern manufacturing. With over two decades of experience in computer-aided engineering (CAE) services, RA Global delivers precise and reliable solutions that enhance product reliability, durability, performance, and stability for clients in India and globally. Our highly experienced engineers possess extensive knowledge across diverse industries, including automotive, heavy structures, and aeronautical, ensuring technically robust outcomes.
Combining innovation and quality, RA Global leverages cutting-edge 3D scanning and reverse engineering technologies to capture complex geometries, recreate existing components, and optimize designs for performance and manufacturability. As a trusted 3D modeling studio, we also offer comprehensive 3D designing services in Mumbai and across India, including industrial 3D modeling, rapid 3D model development, 3D product modeling, architectural models, and customized 3D rendering services.
Our team provides precise 2D & 3D CAD drawings and 2D and 3D CAD drafting services, ensuring accurate design interpretation, seamless assembly validation, and smooth production workflows. Our 3D CAD modeling services deliver accurate geometry, optimized designs, and precise dimensions, helping businesses reduce development time and improve product quality. Backed by advanced CAD tools and extensive expertise, RA Global is recognized as one of the best CAD design service providers, delivering reliable, scalable, and cost-effective solutions for diverse industries. With a customer-centric approach, pan-India reach, and commitment to innovation, RA Global ensures every project exceeds expectations, offering sustainable, high-quality engineering outcomes.
3D scanning and reverse engineering are more than supporting technologies; they are critical enablers of modern, data-driven manufacturing. By mastering the technical workflows from scanning to CAD to additive manufacturing, RA Global provides end-to-end solutions that shorten development cycles, reduce risk, and deliver precision at scale. With RA Global's expertise in 3D scanning and reverse engineering, organizations can unlock new levels of efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness in their manufacturing operations.
A lights-out factory, often referred to as a dark factory, runs with little to no human presence, enabling it to operate autonomously without on-site human intervention, essentially functioning in the dark. As industries look towards the "factory of the future," autonomous manufacturing in these settings is anticipated to expand across various sectors.
Dark factories, also known as "lights-out factories," are revolutionizing the manufacturing industry with cutting-edge automation technologies. These facilities operate without human intervention, leveraging AI-driven robotics, IoT networks, and intelligent automation protocols to ensure seamless 24/7 operation with minimal energy consumption.
India is moving towards dark factories, but challenges remain. The country's manufacturing sector is expected to embrace partial dark factory operations within the next 7-10 years, with fully autonomous, AI-powered factories likely emerging in 15-20 years. Key sectors that will drive this transformation include semiconductors, AI-driven technologies, automation, IoT, and robotics.

3D Scanning and Reverse Engineering: For precise geometrical digital models for automated production lines. Component Recreation: Reverse engineering uses 3D scan data to recreate digital models of physical parts for manufacturing.
Applications in Dark Factories
Product Design and Development: Creating innovative products with optimized performance and reduced costs.
In dark factories (lights-out factories), product design and development leverage advanced technologies to enable autonomous manufacturing and optimization.
Key Aspects
Technologies Enabling Dark Factory Product Development
Long-Range 3D Scanning and As-Built Documentation:
Technologies Involved-
By leveraging these services and technologies, India can navigate the transition to smart manufacturing and capitalize on the benefits of dark factory automation.
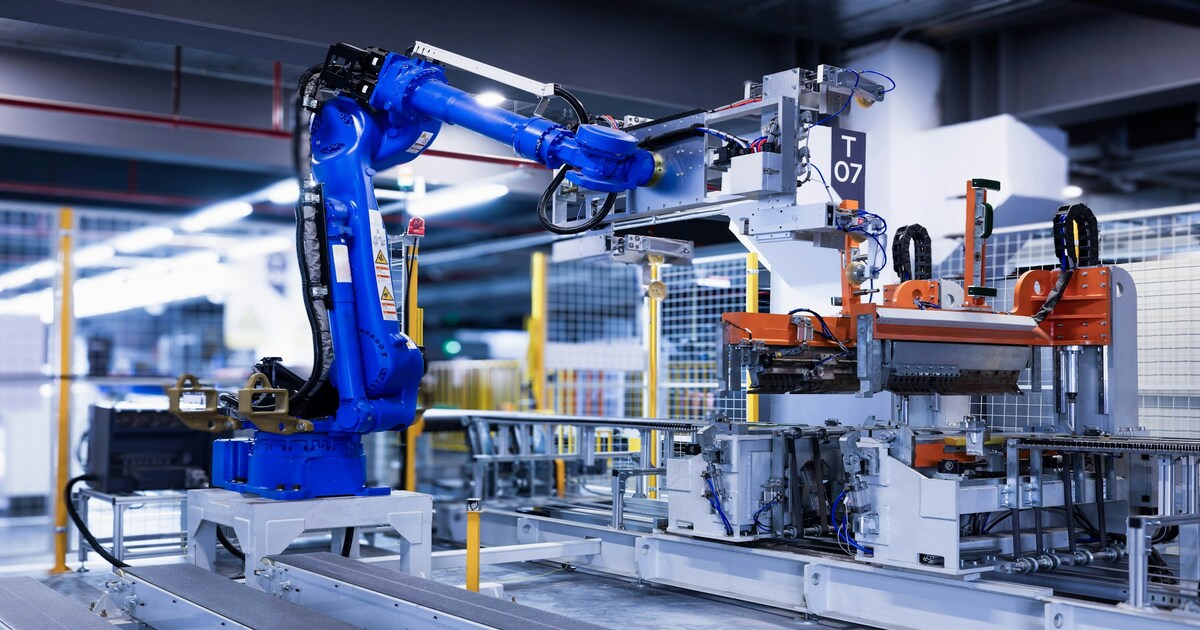

As India moves towards embracing dark factory technologies, it's clear that this revolution in automated manufacturing will bring about significant changes. With benefits like increased efficiency, cost savings, and improved safety, dark factories are poised to transform the manufacturing landscape. RA Global's services, including 3D scanning, CAD design, product development, and database architecture, can help Indian companies navigate this transition and thrive in the era of smart manufacturing. By leveraging these technologies and services, India can capitalize on the benefits of dark factory automation and emerge as a leader in the global manufacturing sector.
Source: google.com
Improvement in previously designed products is required to increase the usability of certain products. Some products in current use were designed with no design data stored, such as their physical or digital drawings, to refer to for making advancements in current products in use. Some products with small and complex features and internal designs are difficult to observe or measure; with no digital data on design, it becomes difficult for design upgrades. In such cases, 3D reverse engineering services are crucial for product design improvement or new product development. 3D scanning and reverse engineering are impressive processes for improvement in product design or product development and play a vital role.
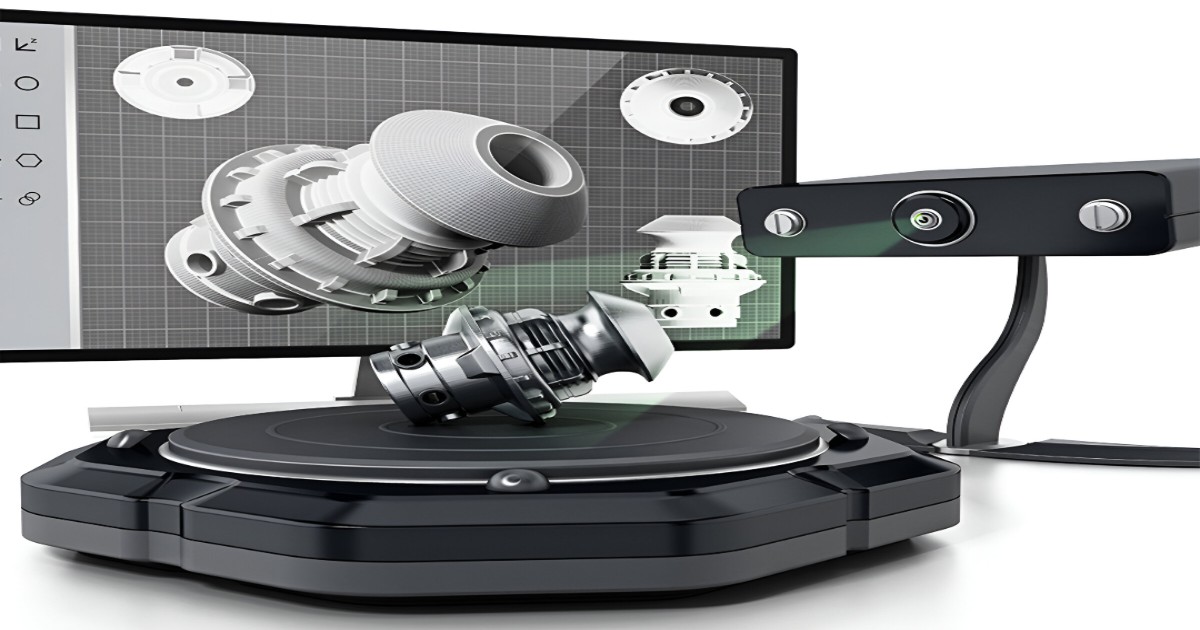

3D scanning is a process of analyzing a real-world object or an environment to collect data on its shape, color, and possibly its appearance. The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models.
The data obtained as the output is point cloud data, which is worked upon with various tools to obtain a solid 3D model. The 3D scanner has a somewhat characteristic feature of capturing the shape and color data of the objects.
In most cases, multiple 3D scans are required for products from different angles to collect data on their shapes from different sides, and these scans are combined to give actual point cloud data of an object, which replicates the shape of an object or makes some modifications in the product design to develop a new product out of it.
The common applications of this technology include product design or development, manufacturing, augmented reality, motion capture, gesture recognition, robotic mapping, industrial design, orthotics, and prosthetics. Reverse engineering and prototyping, quality control/inspection, and digitization of cultural artifacts are some of its other applications. These data are extensively used in the entertainment industry in the production of movies and video games, including virtual reality.
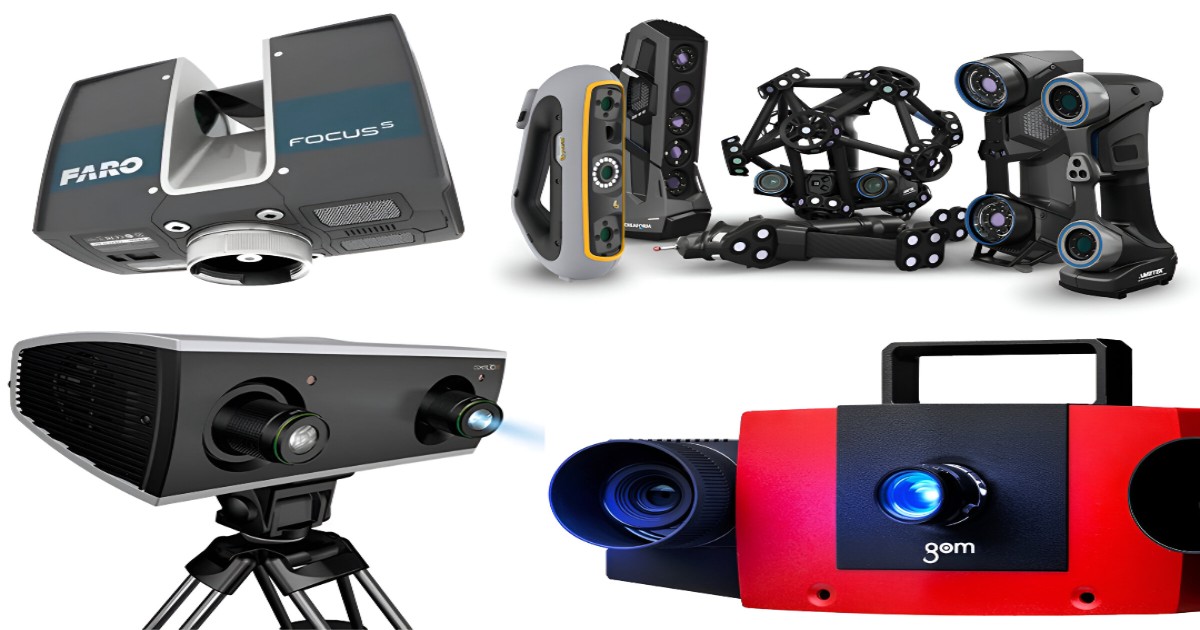
The type of scanning technique to be used depends on product size, the complexity of design, and the accuracy of output required. The accuracy of the 3D scanner for general-purpose use is 0.01mm to 0.1mm. 3D scanners can be contact types, like probe-based, or non-contact types, like portable and handheld 3D laser scanners.

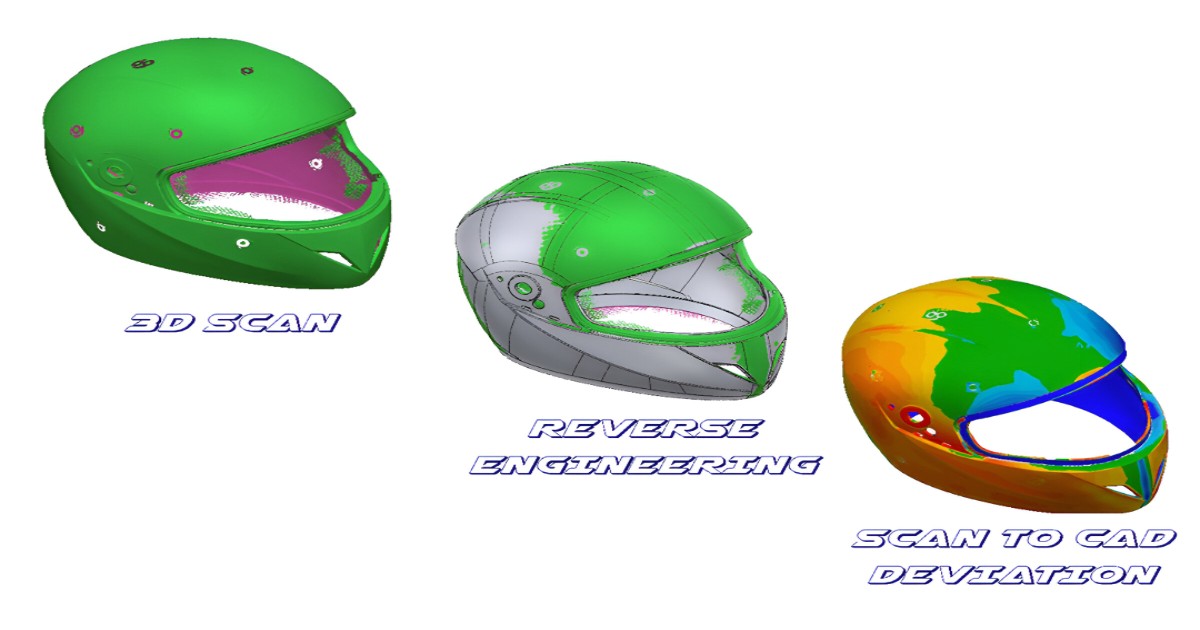
The point cloud data obtained through 3D scanning is not of much use until the solid model based on the data is constructed using reverse engineering services. The STL format point cloud data is cleaned for the noise with unwanted data removed, and the data is aligned with the surface for ease of various operations to create a solid 3D model. Various textures and colors can also be captured by 3D scanning and modeled accordingly to replicate the available solid product. This technique helps in easing the measurement task on a product that is difficult due to its size or its location.

© 2026 RA Global Tech Solutions
Site design and developed by Rajkar Global