SLS 3D Printing: Selective Laser Sintering
What is SLS 3D printing?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an industrial additive manufacturing technology that uses a high-power laser to fuse polymer powder into solid, functional 3D parts. SLS builds components layer by layer without the need for support structures, making it ideal for complex geometries, lightweight designs, and end-use functional parts.
SLS is widely used in engineering, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, consumer goods, and tooling applications due to its excellent mechanical strength, durability, and design freedom. Its ability to produce near-isotropic parts with high dimensional accuracy makes it one of the most trusted technologies for production-grade polymer components.
SLS is required for users seeking a solution for manufacturing functional goods with complex geometries. This technology has little to no restrictions compared to other 3D printing services.
Key Aspects of SLS 3D Printing
- Powder-based polymer sintering process
- No support structures required
- High mechanical strength and durability
- Excellent dimensional accuracy
- Suitable for small-batch production and end-use parts
- Wide range of engineering materials (mostly nylon-based)
- Ideal for complex geometries and lightweight structures
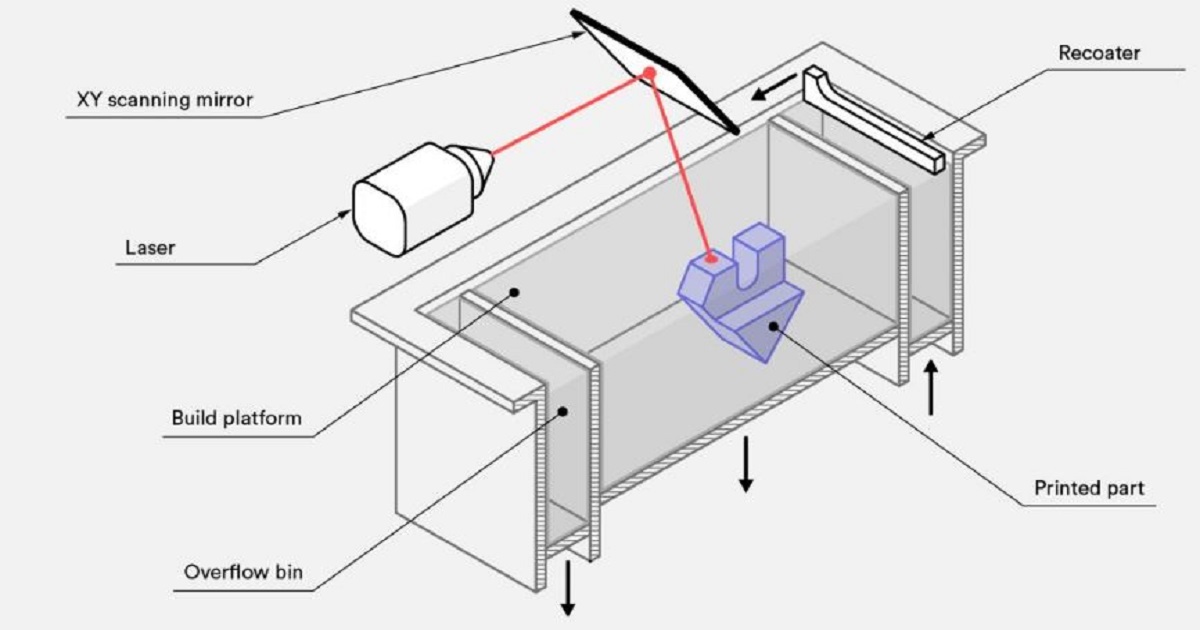
How does SLS printing work?
- Powder Bed Preparation: A thin layer of powdered material (e.g., nylon) is evenly spread across the build platform. The powder might be preheated to near its melting point to reduce the energy required for sintering.
- Selective Laser Sintering: A high-power laser scans the powder surface following the cross-section defined by the 3D model. Wherever the laser hits, the powder particles are fused (sintered) together to form a solid layer.
- Layer-by-Layer Build: After one layer is sintered, the build plate lowers slightly, and a new layer of powder is spread over the previous layer. The laser then sinters the next cross-section. This cycle repeats until the entire part is complete.
- Cooling: Once printing is done, the build remains within the powder bed to cool down gradually. Controlled cooling helps prevent warping and internal stress, improving dimensional stability.
- Depowdering and Post-Processing: The unsintered powder is removed (often recovered for reuse), and the parts may undergo post-processing such as sandblasting, smoothing, dyeing, or other finishing as required.
Types of materials used in SLS 3D printing
- PA12 Nylon: It is a widely used SLS material known for its high strength, stiffness, and excellent chemical resistance. It offers stable mechanical performance under continuous load, making it highly reliable for functional applications. With its balance of durability and dimensional accuracy, PA12 is ideal for producing functional prototypes, snap-fit features, enclosures, and various end-use mechanical parts that require strength, precision, and long-term stability.
- PA11 Nylon: It is a high-performance SLS material recognized for its superior elasticity, impact resistance, and ability to withstand repeated stress without cracking. Its flexibility makes it ideal for thin-walled, lightweight, or complex designs that require both durability and adaptability.
- PA12 Glass-Filled: It is a specialized SLS material engineered for applications that demand enhanced rigidity and structural integrity. Reinforced with glass beads, it offers superior stiffness, improved heat resistance, and excellent dimensional stability compared to standard PA12.
SLS 3D printing capabilities
- Maximum Build Size: 395 mm x 500 mm x 395 mm
- Standard Lead Time: 4 Business Days
- Dimensional Accuracy: ± 0.3% with a lower limit of ± 0.3 mm
- Layer Height: 100 μm
Design Guidelines for SLS 3D printing
- Wall Thickness: 0.7 mm for Nylon PA12
- Supported walls: 0.7 mm
- Minimum feature size: 0.8 mm
- Minimum hole diameter: 1.5 mm
Benefits of SLS 3D Printing
- Complex Geometries: SLS can produce complex geometries and intricate details.
- No Support Structures: SLS doesn't require support structures, as the powder bed provides support.
- Strong Parts: SLS parts can be strong and durable.
- Material Versatility: SLS can work with various materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
Application of SLS 3D Printing
- Aerospace: SLS is used in aerospace for producing complex components.
- Automotive: SLS is used in automotive for producing prototypes, production parts, and tooling.
- Medical: SLS is used in medicine for producing custom implants, surgical models, and medical devices.
- Industrial: SLS is used in various industrial applications, such as producing complex components and tooling
Additionally, the number of materials that may be used in SLS production is constrained, making it unsuitable for many applications. We manufacture your parts according to strict manufacturing standards. Verification of these requirements is included in our inspection report that is shipped with every order.
UPLOAD your design for an Instant Quote (Acceptable file types are .stl, .step, and .x_T.)
Frequently Asked Questions
What is SLS 3D Printing?
SLS is a powder bed fusion technique where a powerful laser selectively sinters (fuses) fine polymer powder particles, layer by layer.
What are the key materials used in SLS?
The most common material is nylon (PA12, PA11), which produces strong, durable, and chemically resistant parts. Other materials include flame-retardant polymers and flexible TPE/TPU.
What is the major advantage of using SLS?
The primary advantage is design freedom because the powder supports the entire part. This allows for complex geometries, internal features, and nesting of multiple parts in a single build, maximizing efficiency.
Is SLS suitable for end-use parts?
Yes. SLS is an ideal technology for low- to medium-volume functional parts and prototypes that require high mechanical strength, excellent fatigue resistance, and durability.
What is the typical surface finish of SLS parts?
SLS parts have a characteristic slightly rough, grainy surface texture straight off the machine. They can be dyed or finished (e.g., tumbled or polished) to improve aesthetics and seal the porous surface.

