Investment Casting
What is investment casting?
Investment casting is a manufacturing technique where a wax pattern is covered with a refractory ceramic material. Once the ceramic material has dried and hardened, the wax is melted and removed, leaving behind a cavity that matches the final product's geometry. Molten metal is then poured into this cavity, which cools and solidifies to form the metal casting. The ceramic shell is subsequently removed from the metal, resulting in a near-net precision metal component. This method is widely used across various industries due to its ability to produce complex parts with precise dimensions and a smooth surface finish.
Investment casting, a precision technique also known as lost wax casting, boasts a rich history spanning decades. This manufacturing process involves creating a wax pattern that shapes a disposable ceramic mold, ideal for producing intricate metal parts in various shapes at scale. The wax model accurately represents the final product, offering several advantages. It yields parts with superior surface finish, tight tolerances, and complex designs, making it indispensable across industries like marine engineering, aerospace, and automobile assembly. Its capability to produce detailed parts with minimal secondary operations underscores its value in modern manufacturing.
Key Aspects of investment casting:
- Complex Geometries: Investment casting allows for the creation of complex shapes and geometries with high accuracy.
- High Precision: The process produces parts with tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes.
- Material Versatility: Investment casting can be used with a wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium.
- Low Tooling Costs: Unlike other casting methods, investment casting does not require expensive tooling, making it ideal for low-volume production.
- Reduced Material Waste: The process generates minimal waste, making it a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option.
Why is investment casting important?
Investment casting plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing by bridging the gap between complex design requirements and high-precision production, making it a preferred method across industries such as aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, defense, and medical equipment. This process allows engineers to produce intricate components with tight tolerances that traditional casting or machining methods cannot achieve efficiently. Investment castings come out with near-net shapes and smooth surface finishes, reducing the need for extensive machining and post-processing, which in turn saves time and cost.
The process supports a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and exotic alloys, enabling manufacturers to meet specific performance demands such as heat resistance and corrosion protection. With its repeatable and precise methodology, investment casting ensures uniformity and high quality across batches, while also minimizing material waste and promoting sustainability through the use of recycled metals.
What are the common challenges in investment casting?
Investment casting can present several challenges, including maintaining dimensional accuracy due to shrinkage and deformation, managing porosity and defects that can form during solidification, and achieving a smooth surface finish, particularly for complex geometries. Material limitations, longer lead times, and higher costs compared to other manufacturing processes can also be significant hurdles. Additionally, creating accurate and durable patterns and preventing shell cracking during the casting process are crucial to ensuring part quality and minimizing production issues.

Related Services
- 3D Scanning and Reverse Engineering: Accurately replicate existing components or create precise digital models for new designs.
- CAD Modeling and Simulation: Optimize wax patterns, mold designs, and metal flow to minimize defects and improve efficiency.
- Product Development Services: Ensure complex castings are functional, durable, and manufacturable.
- CMM Inspection and Metrology: Guarantee dimensional accuracy and compliance with international quality standards.
- Material Selection and Surface Finishing: Help clients choose the right alloys and finishing methods for superior performance.
- Post-Processing Support: Assist with polishing, machining, or coating to achieve final specifications.
- Sustainability and Waste Management: Implement eco-friendly practices to reduce material waste and improve cost efficiency.
The Process
Investment casting is a complex production method that produces finely detailed metal parts. In this process, there are 9 steps involved
- Wax Making: A wax pattern is made, which is then used to inject the wax material into the aluminum mold, resulting in the exact shape and dimensions of the final product. This wax pattern serves as the base for the whole casting procedure.

- Wax Assembly: These patterns are mounted on a pouring cup and joined by a "gate" to a central wax stick known as a "tree" or "sprue" to form a casting cluster or assembly.
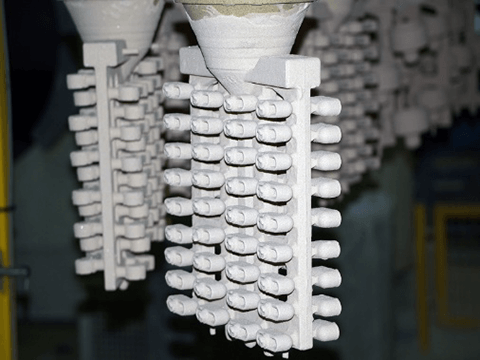
- Investment: In this method, the pattern assembly is dipped into ceramic slurry until multiple layers of refractory materials are applied. Note that before applying the next layer, each layer needs to be sufficiently dry. This may result in a thick, robust ceramic shell that protects the delicate wax designs.

- De-waxing: After the ceramic dries, the wax is melted in an autoclave to leave the assembly inside the shell in negative form. After that, the shell mold is burned in an oven at a high temperature

- Casting: A molten metal is injected into the shell using a variety of materials and techniques. As the metal cools, the parts, gates, tree, and pouring cup solidify into castings.

- Knock Out: Vibration or water blasting is used to break off the ceramic shell after the metal has cooled and solidified.

- Cut Off: Parts are cut away from the central tree using a high-power saw blade.
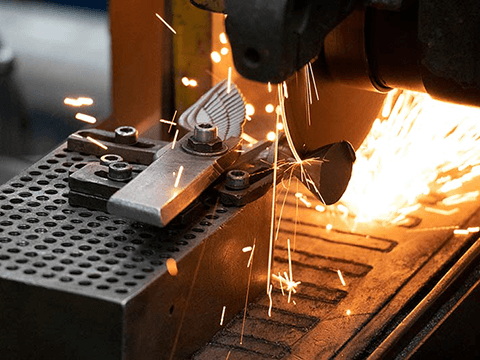
- Finishing: In order to create a metal casting that is exactly like the original wax pattern, minor finishing procedures like fettling and grinding are performed.

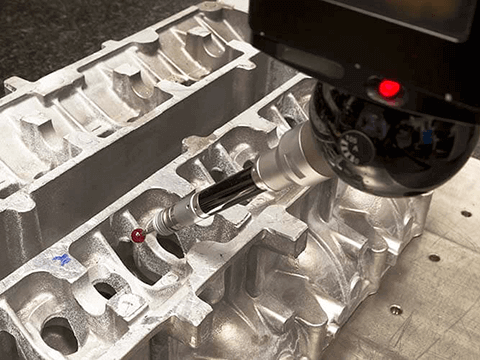
- Inspection: The completed part will next be examined with gauges, calipers, a CMM, or 3D laser scanning for additional analysis to look for surface flaws and imperfections.
What are the applications of investment casting across various industries?
Investment casting is a versatile manufacturing process used to produce precise and complex metal components. Its applications span across multiple industries, including:
- Aerospace Industry: Manufacturing turbine blades, engine components, brackets, and landing gear parts where high precision and strength are critical.
- Automotive Industry: Producing engine blocks, transmission components, gear housings, and custom car parts with tight tolerances and superior surface finish.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Creating valves, pump components, and fittings that can withstand high pressure, temperature, and corrosive environments.
- Power Generation: Producing turbine components, pumps, and other critical parts used in thermal, nuclear, and renewable energy systems.
- Medical Equipment: Manufacturing surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and dental components that require exact dimensions and biocompatible materials.
- Industrial Machinery: Producing high-strength gears, impellers, and other machinery components where durability and reliability are essential.
- Defense and Military: Fabricating complex parts for firearms, armored vehicles, and other defense equipment requiring high performance under extreme conditions.
- Marine Industry: Producing propellers, pump housings, and other corrosion-resistant components for ships and offshore platforms.
Why Choose RA Global?
We offer premium investment cast parts in a range of ferrous and non-ferrous alloys. We also perform the necessary secondary operations, such as heat treatment, finish machining, and surface treatment, on the cast pieces
RA Global can work with carbon steel, low-alloy steel, stainless steel grades, and a wide variety of non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, brass, and bronze. The management team consists of a flexible team of dedicated, technically and commercially sound, experienced, and seasoned managers who enable the delivery of superior goods and services.
- Expertise: Skilled engineers and designers with industry-leading 3D CAD software expertise
- Precision: High-quality 3D models tailored to specific needs, improving product design and development
- Collaboration: Streamlined communication among team members and stakeholders
Frequently Asked Questions
What is investment casting?
It’s a precision manufacturing process that creates complex metal parts by pouring molten metal into ceramic molds formed around wax patterns.
Why choose RA Global for investment casting?
We deliver high‑quality cast parts with fine detail, tight tolerances, and smooth finishes, supported by expert engineering and strict quality control.
Which industries use investment casting?
Aerospace, automotive, industrial machinery, medical devices, and energy sectors benefit from durable, complex, and lightweight metal parts made this way.
What materials can you cast?
Stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, bronze, and specialized alloys based on your project’s strength, temperature resistance, and design needs.
Can you produce both prototypes and production runs?
Yes! We support small batches for prototyping and scalable production volumes to meet diverse customer requirements efficiently.

