Finite Element Analysis Services
What is finite element analysis?
Finite Element Analysis is a simulation method where complex mechanical structures under various loading and boundary conditions are broken down into finite elements, and complex engineering calculations are solved using FEA software. FEA is a proven method that solves real-world forces like stress, temperature, dynamic loading, and fluid pressure by breaking them into smaller finite elements. This helps engineers predict performance, behaviour, optimize designs, and cut costs on physical testing.
The Finite Element Method is a powerful numerical technique used to solve complex engineering problems involving differential equations, calculus-based formulations, inverse matrix methods, and Laplace transforms under various loading and boundary conditions. FEM enables accurate prediction of structural stress, deformation, temperature distribution, fluid flow, dynamic response, and thermal behavior across components and systems.
At RA Global, we provide comprehensive Finite Element Analysis services, including static and stress analysis, thermal analysis, seismic analysis, vibration analysis, and computational fluid dynamics.
Key aspects of finite element analysis services:
Here are some key aspects of finite element analysis services:
- FEM: FEM is mathematical engineering calculation for solving different loading and boundary condition for a part or system. FEA simulates real-world conditions and reducing the need for physical prototypes.
- Accuracy: FEA provides detailed simulations, enabling accurate predictions of a product’s or system’s behaviour.
- Optimization: FEA helps optimize designs for best performance, durability with value addition.
- Analysis Types: Various analysis types, such as static, dynamic, thermal, and modal analysis.
- Complex Geometries: FEA breaks down complex geometries and systems into discretized conditions for simulation.
FEA services support the development of complex products and systems, enabling businesses to create innovative, efficient, and reliable solutions.
Why are finite element analysis services important?
FEA services boost product reliability, optimize designs, ensure safety standards, predict behaviour under various loads and boundary conditions, enabling complex simulations of intricate geometries, making it essential for creating reliable, efficient, and cost-effective products across industries like aerospace, automotive, heavy industry, and civil engineering. By simulating real-world conditions, FEA helps identify potential failures, optimize designs, and ensure safety and compliance with regulatory requirements. It also improves product performance, efficiency, and lifespan while reducing material waste. Ultimately, FEA accelerates the design process, enabling industries to bring products to market faster and gain a competitive edge.
What are the common challenges in finite element analysis?
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) presents several challenges, including ensuring accurate mesh generation and mesh size, accurately representing complex material behaviour, and applying realistic boundary conditions. Achieving convergence in simulations and accurately interpreting results can also be difficult. Additionally, validating FEA models against experimental data and managing complex geometries and intricate boundary challenges. Furthermore, computational time and resources can be significant hurdles. Addressing these challenges requires expertise, experience, and adherence to FEA best practices.
Related Services
Some related services to Finite Element Analysis include:
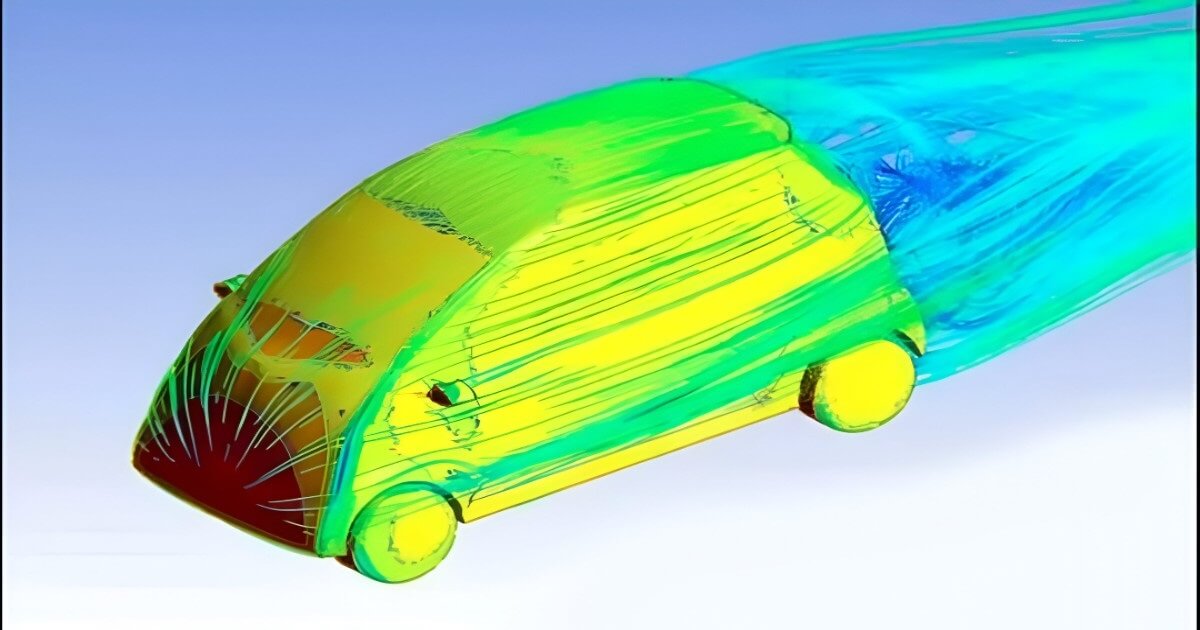
- Computational Fluid Dynamics: It is a powerful engineering tool that uses numerical methods to simulate fluid flow, heat transfer (convection, conduction, and radiation), and fluid-structure interactions, solving complex physics problems by modeling governing equations to predict behavior in systems. It is applicable for Automobile, Aeronautical, Submarines, Pressure vessels and Home appliances Industries. CFD help OEM and manufactures to reducing reliance on expensive physical tests.
- Structural Analysis: Structural analysis is the backbone of applied mechanics and civil engineering, focusing on predicting the performance and behaviour of structures the skeleton of machines or civil structures like buildings, bridges, and tunnels, when subjected to external forces and environmental loads.
- Thermal Analysis: Thermal analysis studies material properties changing with temperature, using CAE techniques to measure heat flow/mass changes and engineering simulations to predict heat transfer in products, ensuring performance, preventing failure, and optimizing cooling in electronics, aerospace, vehicles and pressure vessels.
- Dynamic Analysis: Dynamic analysis studies how structures and mechanical systems respond to time-varying forces and motions, unlike static loads. It's crucial for ensuring designs withstand real-world conditions, especially in environments with seismic activity, motion, resonance, vibration, and wind pressure. It's applicable to civil structures like buildings and bridges, automotive, aerospace, home appliances, and electronics when subjected to external forces and environmental loads.
- Modal Analysis: It is a key engineering technique that identifies a structure's intrinsic vibration characteristics: its natural frequencies and corresponding mode shapes, crucial for preventing resonance-induced failure by matching external forces to these inherent properties, ensuring structural integrity, and optimizing design for dynamic loads like wind or seismic events.
- Optimization: Optimization in design uses computer simulation to test virtual prototypes and inform engineering decisions, which helps guide design parameters and topology for improved performance.
- Multi-Body Dynamics: It is an advanced engineering simulation method that models and analyzes complex systems with interconnected moving parts, predicting their motion, forces, and interactions to optimize design, reduce prototypes, and improve performance in industries like automotive, robotics, and aerospace by understanding how components work together under forces and constraints.
Finite Element Analysis is typically complemented by a range of other engineering simulation services to provide a holistic approach to product development.
The Process
The Finite Element Analysis process typically involves pre-processing, simulation and post-processing:
Pre-processing is the initial and most critical phase of finite element analysis, where the physical system is prepared for numerical simulation. Key activities include:
- Geometry Creation or Import: Developing or importing the 3D CAD model of the component or system to be analyzed.
- Material Property Assignment: Defining material characteristics such as Young’s modulus, Poisson’s ratio, and density to accurately represent real-world behavior.
- Meshing: Breaking down complex geometries into smaller, manageable finite elements. Mesh quality and density play a vital role in determining simulation accuracy and computational efficiency.
- Loads and Boundary Conditions: Applying real-world forces, pressures, temperatures, contacts and constraints such as fixed supports or prescribed displacements that the model will experience during operation.
Simulation: During the simulation stage, the FEA software performs the core calculations. Using the inputs from pre-processing, the solver computes the governing equations that define the system’s physical behavior, such as structural response, heat transfer, or fluid flow. The software assembles equations for each finite element and solves the resulting large system of algebraic equations to determine unknown parameters, including nodal displacements, stresses, or temperatures.
Post-Processing: Post-processing focuses on evaluating and interpreting the simulation results to support engineering decisions. The numerical output is converted into meaningful visual and analytical data, including:
- Result Visualization: Graphical outputs such as contour plots displaying stress distribution, deformation, temperature variations, or flow patterns.
- Result Interpretation: Identification of critical values such as von-mises stresses, safety factors, deflection and natural frequencies.
- Verification and Validation: Reviewing results to confirm accuracy, ensure compliance with design requirements, and determine whether further design iterations are needed.
This process helps engineers and analysts simulate and optimize product performance, identify potential issues, and improve design reliability.
Advantages of utilizing finite element analysis services:
- Enhanced Product Safety: Finite element analysis aids engineers in identifying vulnerabilities in their product designs, thereby helping to prevent collapses and accidents.
- Improved Product Performance: Finite element analysis can be leveraged to optimize product designs for superior performance, encompassing aspects like weight reduction, fuel efficiency, and noise reduction.
- Cost Reduction: Finite element analysis assists engineers in identifying areas for cost savings, such as the use of lightweight materials or straightforward designs.
- Accelerated Product Development: Finite element analysis serves as an invaluable tool to streamline the product development cycle by minimizing the necessity for physical prototypes.

What are the applications of finite element analysis services across various industries?
- Aerospace: FEA is an advanced numerical simulation technique that enables engineers to accurately evaluate how complex aerospace components such as wings, fuselages, turbine blades, and landing gear respond to real-world physical conditions, including high temperatures, vibrations, and heavy structural loads.
- Automotive:Finite Element Analysis plays a vital role in modern automotive design by enabling virtual crash simulations to enhance occupant safety, optimizing lightweight structural components, evaluating thermal performance of complex electronics such as EV batteries, reducing noise, vibration, and harshness, and accurately predicting real-world behavior thereby minimizing physical prototypes, lowering costs, and shortening development timelines.
- Medical Research: Finite Element Analysis is an advanced simulation technique used in medical device development to predict how products behave under real-world forces, enabling optimization for safety, durability, and user comfort.
- Consumer Goods:FEA is an advanced computer-based simulation technique that engineers use to predict how products respond to real-world physical effects such as forces, vibrations, heat, fluid flow, and other physical phenomena.
- Civil and Architectural Industries: Finite Element Analysis is a widely used simulation technique in the civil and architectural sectors to evaluate and predict how building structures perform under different loading and environmental conditions.
- Energy and Nuclear: Finite Element Analysis is an essential tool in the energy and nuclear industries, allowing engineers to conduct in-depth evaluations of complex structures, assess component performance under extreme operating conditions, and identify potential failures before they arise.
- Defense: Finite Element Analysis is a vital tool in the defense sector, widely used to evaluate and ensure the structural integrity, performance, and safety of military equipment and systems.
Classification of finite element analysis
FEA analysis can be categorized into various types. Some of the most common analysis types include
- Static Analysis:Static analysis in engineering particularly in structural analysis and finite element analysis evaluates how a product responds to steady, time-independent loads such as gravity or self-weight. It examines deformation, internal forces , and displacements to ensure the structure remains safe and does not fail under constant loading conditions, without considering dynamic or time-varying effects.
- Thermal Analysis: Thermal analysis is a critical field within engineering and materials science used to model and predict how heat flows through objects. By applying different thermal loads and boundary conditions, engineers can determine the resulting temperature distributions throughout a product.
- Fatigue Analysis:It is an engineering approach used to estimate the lifespan of a product subjected to repeated or cyclic loading before failure occurs. The method focuses on crack initiation and propagation, making it essential for designing durable components such as aircraft structures or automotive springs that experience continuous flexing, vibration, or temperature variations. Techniques such as S–N curves and rainflow counting are commonly applied to achieve accurate and realistic fatigue life predictions.
- Crashworthiness Analysis:Crashworthiness analysis evaluates a product’s ability to protect occupants during impact events by studying its structural response, energy absorption capability, and the forces transmitted to occupants. Using simulation techniques such as FEA, along with physical testing, this analysis is critical for enhancing safety in vehicles and aircraft.
- Acoustic Analysis: It is used to evaluate quality, identify defects, ensure safety, and comply with industry standards by analyzing noise and vibration through tools such as microphones. This approach supports predictive maintenance, product design optimization, and regulatory compliance by interpreting sound signatures to detect issues ranging from minor flaws to serious structural defects.
How can RA Global assist you?
RA Global Tech Solutions is a leading finite element analysis service provider in India and across the globe for various industries. We offer comprehensive FEA services as well as FEM analysis. Our team of experienced engineers possesses extensive knowledge across diverse industries. RA Global FEA services can help enhance product design, safety, and performance. RA Global offers FEA services at affordable charges in India, helping clients enhance product reliability, durability, performance, and stability. Our team of experienced engineers uses the latest technological advancements to deliver precise and sustainable results.
- Expertise: Highly skilled CAE services professionals across automotive, heavy structures, and aeronautical.
- Quality: RA Global focuses on delivering high-quality results by understanding how components behave under various loading conditions.
- Innovation: As the RA Global team of innovative experts, we are using cutting-edge FEA software and techniques to deliver innovative solutions.
- Customer-centric approach: RA Global prioritizes client satisfaction, communication, and collaboration to meet their needs.
- Pan-India reach: We offer Computer-Aided Engineering services in multiple cities across India, ensuring smooth, consistent, and timely project execution, regardless of the client’s location.
Ra Global offers top-tier FEA services that boost your products' reliability, durability, performance, and stability. Our team of experts consistently strives to exceed productivity expectations, providing customers with an unparalleled experience.
Contact us today to discover how RA Global can elevate your product reliability and performance through our exceptional FEA services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is finite element analysis (FEA)?
FEA is a simulation technique that predicts how products or structures react to real-world forces, vibration, heat, and other physical effects.
Why choose RA Global for FEA services?
We combine expert engineers, advanced simulation tools, and industry knowledge to deliver reliable analysis that supports design optimization and risk reduction.
Which industries use FEA?
Automotive, aerospace, industrial equipment, consumer products, and civil engineering rely on FEA to validate designs and improve product performance.
What can you analyze with FEA?
We analyze stress, strain, thermal performance, deformation, fatigue, vibration, and more to identify potential issues before physical prototyping.
What deliverables do you provide?
We deliver detailed reports, simulation results, recommendations, and visual outputs that help guide design decisions and improve product reliability.

